与表面夹爪互动#
本教程展示了如何在仿真中与连接到其末端执行器的关节机器人进行交互。这是 与关节交互 教程的延续,我们在那里学习了如何与关节机器人进行交互。请注意,截至 IsaacSim 5.0,仅支持在cpu后端上的表面夹爪。
代码#
该教程对应于 scripts/tutorials/01_assets 目录中的 run_surface_gripper.py 脚本。
run_surface_gripper.py 的代码
1# Copyright (c) 2022-2026, The Isaac Lab Project Developers (https://github.com/isaac-sim/IsaacLab/blob/main/CONTRIBUTORS.md).
2# All rights reserved.
3#
4# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
5
6"""This script demonstrates how to spawn a pick-and-place robot equipped with a surface gripper and interact with it.
7
8.. code-block:: bash
9
10 # Usage
11 ./isaaclab.sh -p scripts/tutorials/01_assets/run_surface_gripper.py --device=cpu
12
13When running this script make sure the --device flag is set to cpu. This is because the surface gripper is
14currently only supported on the CPU.
15"""
16
17"""Launch Isaac Sim Simulator first."""
18
19import argparse
20
21from isaaclab.app import AppLauncher
22
23# add argparse arguments
24parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Tutorial on spawning and interacting with a Surface Gripper.")
25# append AppLauncher cli args
26AppLauncher.add_app_launcher_args(parser)
27# parse the arguments
28args_cli = parser.parse_args()
29
30# launch omniverse app
31app_launcher = AppLauncher(args_cli)
32simulation_app = app_launcher.app
33
34"""Rest everything follows."""
35
36import torch
37
38import isaaclab.sim as sim_utils
39from isaaclab.assets import Articulation, SurfaceGripper, SurfaceGripperCfg
40from isaaclab.sim import SimulationContext
41
42##
43# Pre-defined configs
44##
45from isaaclab_assets import PICK_AND_PLACE_CFG # isort:skip
46
47
48def design_scene():
49 """Designs the scene."""
50 # Ground-plane
51 cfg = sim_utils.GroundPlaneCfg()
52 cfg.func("/World/defaultGroundPlane", cfg)
53 # Lights
54 cfg = sim_utils.DomeLightCfg(intensity=3000.0, color=(0.75, 0.75, 0.75))
55 cfg.func("/World/Light", cfg)
56
57 # Create separate groups called "Origin1", "Origin2"
58 # Each group will have a robot in it
59 origins = [[2.75, 0.0, 0.0], [-2.75, 0.0, 0.0]]
60 # Origin 1
61 sim_utils.create_prim("/World/Origin1", "Xform", translation=origins[0])
62 # Origin 2
63 sim_utils.create_prim("/World/Origin2", "Xform", translation=origins[1])
64
65 # Articulation: First we define the robot config
66 pick_and_place_robot_cfg = PICK_AND_PLACE_CFG.copy()
67 pick_and_place_robot_cfg.prim_path = "/World/Origin.*/Robot"
68 pick_and_place_robot = Articulation(cfg=pick_and_place_robot_cfg)
69
70 # Surface Gripper: Next we define the surface gripper config
71 surface_gripper_cfg = SurfaceGripperCfg()
72 # We need to tell the View which prim to use for the surface gripper
73 surface_gripper_cfg.prim_path = "/World/Origin.*/Robot/picker_head/SurfaceGripper"
74 # We can then set different parameters for the surface gripper, note that if these parameters are not set,
75 # the View will try to read them from the prim.
76 surface_gripper_cfg.max_grip_distance = 0.1 # [m] (Maximum distance at which the gripper can grasp an object)
77 surface_gripper_cfg.shear_force_limit = 500.0 # [N] (Force limit in the direction perpendicular direction)
78 surface_gripper_cfg.coaxial_force_limit = 500.0 # [N] (Force limit in the direction of the gripper's axis)
79 surface_gripper_cfg.retry_interval = 0.1 # seconds (Time the gripper will stay in a grasping state)
80 # We can now spawn the surface gripper
81 surface_gripper = SurfaceGripper(cfg=surface_gripper_cfg)
82
83 # return the scene information
84 scene_entities = {"pick_and_place_robot": pick_and_place_robot, "surface_gripper": surface_gripper}
85 return scene_entities, origins
86
87
88def run_simulator(
89 sim: sim_utils.SimulationContext, entities: dict[str, Articulation | SurfaceGripper], origins: torch.Tensor
90):
91 """Runs the simulation loop."""
92 # Extract scene entities
93 robot: Articulation = entities["pick_and_place_robot"]
94 surface_gripper: SurfaceGripper = entities["surface_gripper"]
95
96 # Define simulation stepping
97 sim_dt = sim.get_physics_dt()
98 count = 0
99 # Simulation loop
100 while simulation_app.is_running():
101 # Reset
102 if count % 500 == 0:
103 # reset counter
104 count = 0
105 # reset the scene entities
106 # root state
107 # we offset the root state by the origin since the states are written in simulation world frame
108 # if this is not done, then the robots will be spawned at the (0, 0, 0) of the simulation world
109 root_state = robot.data.default_root_state.clone()
110 root_state[:, :3] += origins
111 robot.write_root_pose_to_sim(root_state[:, :7])
112 robot.write_root_velocity_to_sim(root_state[:, 7:])
113 # set joint positions with some noise
114 joint_pos, joint_vel = robot.data.default_joint_pos.clone(), robot.data.default_joint_vel.clone()
115 joint_pos += torch.rand_like(joint_pos) * 0.1
116 robot.write_joint_state_to_sim(joint_pos, joint_vel)
117 # clear internal buffers
118 robot.reset()
119 print("[INFO]: Resetting robot state...")
120 # Opens the gripper and makes sure the gripper is in the open state
121 surface_gripper.reset()
122 print("[INFO]: Resetting gripper state...")
123
124 # Sample a random command between -1 and 1.
125 gripper_commands = torch.rand(surface_gripper.num_instances) * 2.0 - 1.0
126 # The gripper behavior is as follows:
127 # -1 < command < -0.3 --> Gripper is Opening
128 # -0.3 < command < 0.3 --> Gripper is Idle
129 # 0.3 < command < 1 --> Gripper is Closing
130 print(f"[INFO]: Gripper commands: {gripper_commands}")
131 mapped_commands = [
132 "Opening" if command < -0.3 else "Closing" if command > 0.3 else "Idle" for command in gripper_commands
133 ]
134 print(f"[INFO]: Mapped commands: {mapped_commands}")
135 # Set the gripper command
136 surface_gripper.set_grippers_command(gripper_commands)
137 # Write data to sim
138 surface_gripper.write_data_to_sim()
139 # Perform step
140 sim.step()
141 # Increment counter
142 count += 1
143 # Read the gripper state from the simulation
144 surface_gripper.update(sim_dt)
145 # Read the gripper state from the buffer
146 surface_gripper_state = surface_gripper.state
147 # The gripper state is a list of integers that can be mapped to the following:
148 # -1 --> Open
149 # 0 --> Closing
150 # 1 --> Closed
151 # Print the gripper state
152 print(f"[INFO]: Gripper state: {surface_gripper_state}")
153 mapped_commands = [
154 "Open" if state == -1 else "Closing" if state == 0 else "Closed" for state in surface_gripper_state.tolist()
155 ]
156 print(f"[INFO]: Mapped commands: {mapped_commands}")
157
158
159def main():
160 """Main function."""
161 # Load kit helper
162 sim_cfg = sim_utils.SimulationCfg(device=args_cli.device)
163 sim = SimulationContext(sim_cfg)
164 # Set main camera
165 sim.set_camera_view([2.75, 7.5, 10.0], [2.75, 0.0, 0.0])
166 # Design scene
167 scene_entities, scene_origins = design_scene()
168 scene_origins = torch.tensor(scene_origins, device=sim.device)
169 # Play the simulator
170 sim.reset()
171 # Now we are ready!
172 print("[INFO]: Setup complete...")
173 # Run the simulator
174 run_simulator(sim, scene_entities, scene_origins)
175
176
177if __name__ == "__main__":
178 # run the main function
179 main()
180 # close sim app
181 simulation_app.close()
代码解释#
设计场景#
类似于上一个教程,我们在场景中添加了地面平面和一个远处的光源。然后,我们从其 USD 文件中生成一个关节。这次生成了一个拾取-放置机器人。拾取-放置机器人是一个简单的机器人,有 3 个受驱动的轴,其龙门使其可以沿 x 和 y 轴移动,以及沿 z 轴上下移动。此外,机器人末端执行器配备了一个表面夹爪。拾取放置机器人的 USD 文件包含了机器人的几何形状、关节和其他物理属性以及表面夹爪。在自己的机器人上实现类似的夹爪之前,我们建议查看 Isaaclab 的 Nucleus 上找到的夹爪的 USD 文件。
对于抓取和放置机器人,我们使用它的预定义配置对象,在 编写资产配置 教程中可以找到更多信息。对于表面夹爪,我们还需要创建一个配置对象。这可以通过实例化一个 assets.SurfaceGripperCfg 对象并传递相关参数来实现。
可用的参数包括:
max_grip_distance: 夹爪能够抓取物体的最大距离。shear_force_limit: 夹爪能在与夹爪轴线垂直的方向上施加的最大力。coaxial_force_limit: 夹爪沿夹爪轴的方向可以施加的最大力。retry_interval: 夹爪将保持在抓取状态的时间。
如前面的教程中所见,我们可以通过创建一个 assets.Articulation 类的实例,并将配置对象传递给其构造函数,以类似的方式将关节添加到场景中。同样的原则也适用于表面夹爪。通过将配置对象传递给 assets.SurfaceGripper 构造函数,就可以创建表面夹爪并将其添加到场景中。实际上,当按下播放按钮时,对象将只被初始化。
# Create separate groups called "Origin1", "Origin2"
# Each group will have a robot in it
origins = [[2.75, 0.0, 0.0], [-2.75, 0.0, 0.0]]
# Origin 1
sim_utils.create_prim("/World/Origin1", "Xform", translation=origins[0])
# Origin 2
sim_utils.create_prim("/World/Origin2", "Xform", translation=origins[1])
# Articulation: First we define the robot config
pick_and_place_robot_cfg = PICK_AND_PLACE_CFG.copy()
pick_and_place_robot_cfg.prim_path = "/World/Origin.*/Robot"
pick_and_place_robot = Articulation(cfg=pick_and_place_robot_cfg)
# Surface Gripper: Next we define the surface gripper config
surface_gripper_cfg = SurfaceGripperCfg()
# We need to tell the View which prim to use for the surface gripper
surface_gripper_cfg.prim_path = "/World/Origin.*/Robot/picker_head/SurfaceGripper"
# We can then set different parameters for the surface gripper, note that if these parameters are not set,
# the View will try to read them from the prim.
surface_gripper_cfg.max_grip_distance = 0.1 # [m] (Maximum distance at which the gripper can grasp an object)
surface_gripper_cfg.shear_force_limit = 500.0 # [N] (Force limit in the direction perpendicular direction)
surface_gripper_cfg.coaxial_force_limit = 500.0 # [N] (Force limit in the direction of the gripper's axis)
surface_gripper_cfg.retry_interval = 0.1 # seconds (Time the gripper will stay in a grasping state)
# We can now spawn the surface gripper
surface_gripper = SurfaceGripper(cfg=surface_gripper_cfg)
运行仿真循环#
继续从前一教程开始,我们定期重置仿真,为关节设置指令,执行仿真步骤,并更新关节的内部缓冲区。
重置仿真#
要重置表面夹爪,我们只需要调用 :meth:`SurfaceGripper.reset 方法,这将重置内部缓冲区和缓存。
# Opens the gripper and makes sure the gripper is in the open state
surface_gripper.reset()
步进仿真#
将命令应用到表面夹爪涉及两个步骤:
设置所需命令: 这将设置所需的夹爪命令(打开、关闭或空闲)。
将数据写入仿真: 基于表面夹爪的配置,此步骤将转换后的值写入PhysX缓冲区。
在本教程中,我们使用一个随机命令来设置夹爪的指令。夹爪的行为如下:
-1 < command < -0.3 --> 夹爪打开中
-0.3 < command < 0.3` --> 夹爪空闲中
0.3 < command < 1 --> 夹爪关闭中
在每一步中,我们通过调用 SurfaceGripper.set_grippers_command() 方法随机采样命令并将其设置到夹爪中。设置完命令后,我们调用 SurfaceGripper.write_data_to_sim() 方法将数据写入到PhysX缓冲区中。最后,我们进行仿真步进。
# Sample a random command between -1 and 1.
gripper_commands = torch.rand(surface_gripper.num_instances) * 2.0 - 1.0
# The gripper behavior is as follows:
# -1 < command < -0.3 --> Gripper is Opening
# -0.3 < command < 0.3 --> Gripper is Idle
# 0.3 < command < 1 --> Gripper is Closing
print(f"[INFO]: Gripper commands: {gripper_commands}")
mapped_commands = [
"Opening" if command < -0.3 else "Closing" if command > 0.3 else "Idle" for command in gripper_commands
]
print(f"[INFO]: Mapped commands: {mapped_commands}")
# Set the gripper command
surface_gripper.set_grippers_command(gripper_commands)
# Write data to sim
surface_gripper.write_data_to_sim()
更新状态#
要了解表面夹爪的当前状态,我们可以查询 assets.SurfaceGripper.state() 属性。这个属性返回一个大小为 [num_envs] 的张量,其中每个元素都是 -1 、 0 或 1 ,分别对应夹爪的状态。这个属性在每次调用 assets.SurfaceGripper.update() 方法时都会更新。
-1--> 机械手爪是打开的0--> 夹爪正在闭合1--> 夹爪已关闭
# Read the gripper state from the simulation
surface_gripper.update(sim_dt)
# Read the gripper state from the buffer
surface_gripper_state = surface_gripper.state
代码执行#
要运行代码并查看结果,请从终端运行脚本:
./isaaclab.sh -p scripts/tutorials/01_assets/run_surface_gripper.py --device cpu
这个命令应该打开一个带有地面平面、灯光和两个夹取放置机器人的场景。在终端中,您应该看到夹爪的状态以及打印出的命令。要停止仿真,您可以关闭窗口,或在终端中按 Ctrl+C 。
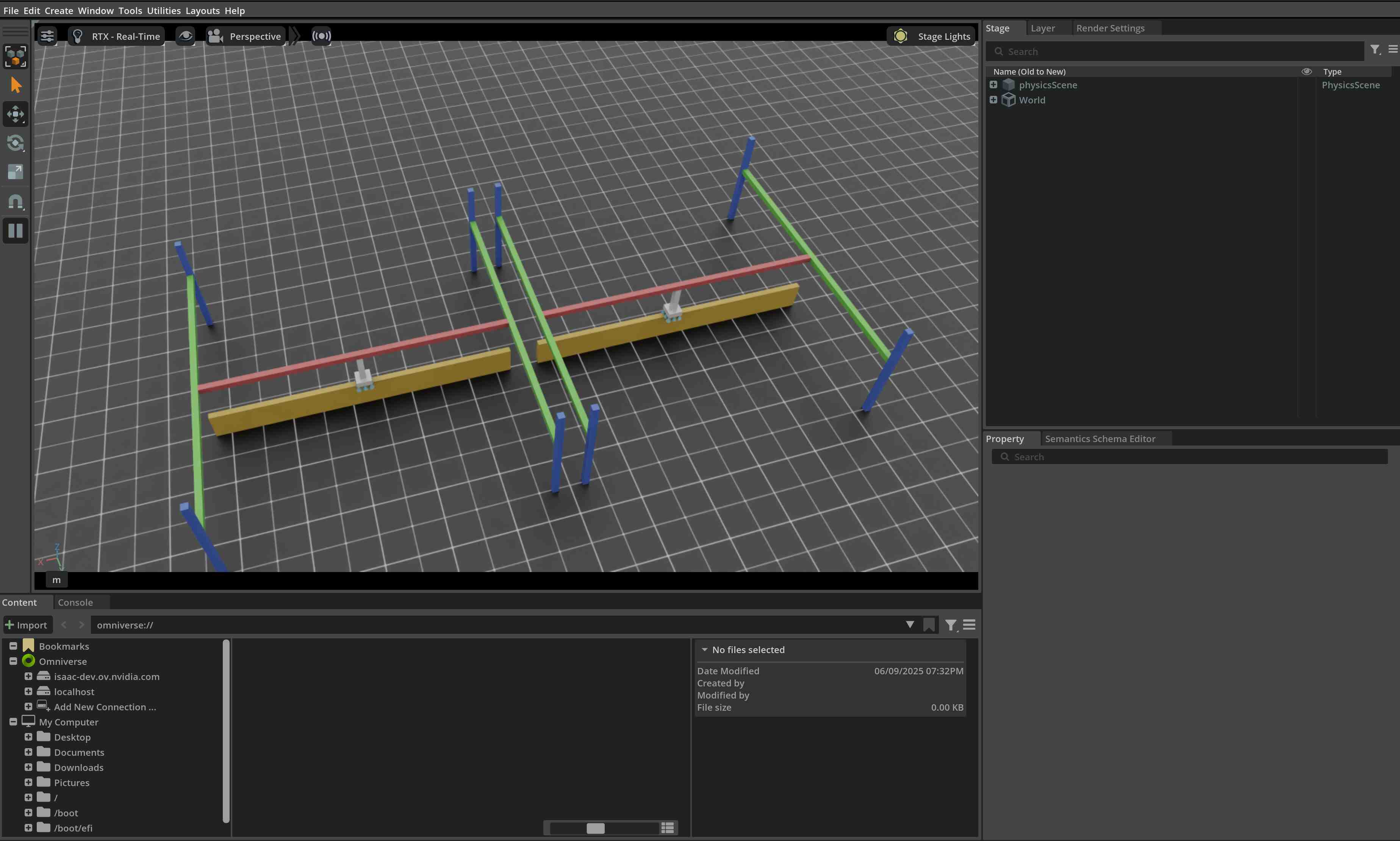
在本教程中,我们学习了如何创建和与表面夹爪进行交互。我们看到如何设置命令并查询夹爪的状态。我们还看到如何更新其缓冲区以从仿真中读取最新状态。
除了本教程之外,我们还提供了一些生成不同机器人的其他脚本。这些脚本包含在 scripts/demos 目录中。您可以这样运行这些脚本:
# Spawn many pick-and-place robots and perform a pick-and-place task
./isaaclab.sh -p scripts/demos/pick_and_place.py
请注意,实践中,用户应该将他们的 assets.SurfaceGripper 实例注册到 isaaclab.InteractiveScene 对象中,在那里会自动处理对 assets.SurfaceGripper.write_data_to_sim 和 assets.SurfaceGripper.update 方法的调用。
# Create a scene
scene = InteractiveScene()
# Register the surface gripper
scene.surface_grippers["gripper"] = surface_gripper
