使用运动空间控制器#
有时,使用差分IK控制器控制机器人的末端执行器姿势是不够的。例如,我们可能想要在任务空间中强制执行非常特定的姿势跟踪误差动态,用关节力/扭矩命令驱动机器人,或者在控制其他方向的运动时在特定方向施加接触力(例如,用布擦洗桌子表面)。在这种任务中,我们可以使用操作空间控制器(OSC)。
操作空间控制的参考资料:
O Khatib. A unified approach for motion and force control of robot manipulators: The operational space formulation. IEEE Journal of Robotics and Automation, 3(1):43–53, 1987. URL http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/JRA.1987.1087068.
Robot Dynamics Lecture Notes by Marco Hutter (ETH Zurich). URL https://ethz.ch/content/dam/ethz/special-interest/mavt/robotics-n-intelligent-systems/rsl-dam/documents/RobotDynamics2017/RD_HS2017script.pdf
在本教程中,我们将学习如何使用OSC来控制机器人。我们将使用 controllers.OperationalSpaceController 类,在其他所有方向上跟踪所需的末端执行器姿态的同时,施加一个垂直于倾斜墙面的恒定力。
代码#
教程对应于 scripts/tutorials/05_controllers 目录中的 run_osc.py 脚本。
run_osc.py的代码
1# Copyright (c) 2022-2026, The Isaac Lab Project Developers (https://github.com/isaac-sim/IsaacLab/blob/main/CONTRIBUTORS.md).
2# All rights reserved.
3#
4# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
5
6"""
7This script demonstrates how to use the operational space controller (OSC) with the simulator.
8
9The OSC controller can be configured in different modes. It uses the dynamical quantities such as Jacobians and
10mass matricescomputed by PhysX.
11
12.. code-block:: bash
13
14 # Usage
15 ./isaaclab.sh -p scripts/tutorials/05_controllers/run_osc.py
16
17"""
18
19"""Launch Isaac Sim Simulator first."""
20
21import argparse
22
23from isaaclab.app import AppLauncher
24
25# add argparse arguments
26parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Tutorial on using the operational space controller.")
27parser.add_argument("--num_envs", type=int, default=128, help="Number of environments to spawn.")
28# append AppLauncher cli args
29AppLauncher.add_app_launcher_args(parser)
30# parse the arguments
31args_cli = parser.parse_args()
32
33# launch omniverse app
34app_launcher = AppLauncher(args_cli)
35simulation_app = app_launcher.app
36
37"""Rest everything follows."""
38
39import torch
40
41import isaaclab.sim as sim_utils
42from isaaclab.assets import Articulation, AssetBaseCfg
43from isaaclab.controllers import OperationalSpaceController, OperationalSpaceControllerCfg
44from isaaclab.markers import VisualizationMarkers
45from isaaclab.markers.config import FRAME_MARKER_CFG
46from isaaclab.scene import InteractiveScene, InteractiveSceneCfg
47from isaaclab.sensors import ContactSensorCfg
48from isaaclab.utils import configclass
49from isaaclab.utils.math import (
50 combine_frame_transforms,
51 matrix_from_quat,
52 quat_apply_inverse,
53 quat_inv,
54 subtract_frame_transforms,
55)
56
57##
58# Pre-defined configs
59##
60from isaaclab_assets import FRANKA_PANDA_HIGH_PD_CFG # isort:skip
61
62
63@configclass
64class SceneCfg(InteractiveSceneCfg):
65 """Configuration for a simple scene with a tilted wall."""
66
67 # ground plane
68 ground = AssetBaseCfg(
69 prim_path="/World/defaultGroundPlane",
70 spawn=sim_utils.GroundPlaneCfg(),
71 )
72
73 # lights
74 dome_light = AssetBaseCfg(
75 prim_path="/World/Light", spawn=sim_utils.DomeLightCfg(intensity=3000.0, color=(0.75, 0.75, 0.75))
76 )
77
78 # Tilted wall
79 tilted_wall = AssetBaseCfg(
80 prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/TiltedWall",
81 spawn=sim_utils.CuboidCfg(
82 size=(2.0, 1.5, 0.01),
83 collision_props=sim_utils.CollisionPropertiesCfg(),
84 visual_material=sim_utils.PreviewSurfaceCfg(diffuse_color=(1.0, 0.0, 0.0), opacity=0.1),
85 rigid_props=sim_utils.RigidBodyPropertiesCfg(kinematic_enabled=True),
86 activate_contact_sensors=True,
87 ),
88 init_state=AssetBaseCfg.InitialStateCfg(
89 pos=(0.6 + 0.085, 0.0, 0.3), rot=(0.9238795325, 0.0, -0.3826834324, 0.0)
90 ),
91 )
92
93 contact_forces = ContactSensorCfg(
94 prim_path="/World/envs/env_.*/TiltedWall",
95 update_period=0.0,
96 history_length=2,
97 debug_vis=False,
98 )
99
100 robot = FRANKA_PANDA_HIGH_PD_CFG.replace(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot")
101 robot.actuators["panda_shoulder"].stiffness = 0.0
102 robot.actuators["panda_shoulder"].damping = 0.0
103 robot.actuators["panda_forearm"].stiffness = 0.0
104 robot.actuators["panda_forearm"].damping = 0.0
105 robot.spawn.rigid_props.disable_gravity = True
106
107
108def run_simulator(sim: sim_utils.SimulationContext, scene: InteractiveScene):
109 """Runs the simulation loop.
110
111 Args:
112 sim: (SimulationContext) Simulation context.
113 scene: (InteractiveScene) Interactive scene.
114 """
115
116 # Extract scene entities for readability.
117 robot = scene["robot"]
118 contact_forces = scene["contact_forces"]
119
120 # Obtain indices for the end-effector and arm joints
121 ee_frame_name = "panda_leftfinger"
122 arm_joint_names = ["panda_joint.*"]
123 ee_frame_idx = robot.find_bodies(ee_frame_name)[0][0]
124 arm_joint_ids = robot.find_joints(arm_joint_names)[0]
125
126 # Create the OSC
127 osc_cfg = OperationalSpaceControllerCfg(
128 target_types=["pose_abs", "wrench_abs"],
129 impedance_mode="variable_kp",
130 inertial_dynamics_decoupling=True,
131 partial_inertial_dynamics_decoupling=False,
132 gravity_compensation=False,
133 motion_damping_ratio_task=1.0,
134 contact_wrench_stiffness_task=[0.0, 0.0, 0.1, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
135 motion_control_axes_task=[1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1],
136 contact_wrench_control_axes_task=[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
137 nullspace_control="position",
138 )
139 osc = OperationalSpaceController(osc_cfg, num_envs=scene.num_envs, device=sim.device)
140
141 # Markers
142 frame_marker_cfg = FRAME_MARKER_CFG.copy()
143 frame_marker_cfg.markers["frame"].scale = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1)
144 ee_marker = VisualizationMarkers(frame_marker_cfg.replace(prim_path="/Visuals/ee_current"))
145 goal_marker = VisualizationMarkers(frame_marker_cfg.replace(prim_path="/Visuals/ee_goal"))
146
147 # Define targets for the arm
148 ee_goal_pose_set_tilted_b = torch.tensor(
149 [
150 [0.6, 0.15, 0.3, 0.0, 0.92387953, 0.0, 0.38268343],
151 [0.6, -0.3, 0.3, 0.0, 0.92387953, 0.0, 0.38268343],
152 [0.8, 0.0, 0.5, 0.0, 0.92387953, 0.0, 0.38268343],
153 ],
154 device=sim.device,
155 )
156 ee_goal_wrench_set_tilted_task = torch.tensor(
157 [
158 [0.0, 0.0, 10.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
159 [0.0, 0.0, 10.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
160 [0.0, 0.0, 10.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
161 ],
162 device=sim.device,
163 )
164 kp_set_task = torch.tensor(
165 [
166 [360.0, 360.0, 360.0, 360.0, 360.0, 360.0],
167 [420.0, 420.0, 420.0, 420.0, 420.0, 420.0],
168 [320.0, 320.0, 320.0, 320.0, 320.0, 320.0],
169 ],
170 device=sim.device,
171 )
172 ee_target_set = torch.cat([ee_goal_pose_set_tilted_b, ee_goal_wrench_set_tilted_task, kp_set_task], dim=-1)
173
174 # Define simulation stepping
175 sim_dt = sim.get_physics_dt()
176
177 # Update existing buffers
178 # Note: We need to update buffers before the first step for the controller.
179 robot.update(dt=sim_dt)
180
181 # Get the center of the robot soft joint limits
182 joint_centers = torch.mean(robot.data.soft_joint_pos_limits[:, arm_joint_ids, :], dim=-1)
183
184 # get the updated states
185 (
186 jacobian_b,
187 mass_matrix,
188 gravity,
189 ee_pose_b,
190 ee_vel_b,
191 root_pose_w,
192 ee_pose_w,
193 ee_force_b,
194 joint_pos,
195 joint_vel,
196 ) = update_states(sim, scene, robot, ee_frame_idx, arm_joint_ids, contact_forces)
197
198 # Track the given target command
199 current_goal_idx = 0 # Current goal index for the arm
200 command = torch.zeros(
201 scene.num_envs, osc.action_dim, device=sim.device
202 ) # Generic target command, which can be pose, position, force, etc.
203 ee_target_pose_b = torch.zeros(scene.num_envs, 7, device=sim.device) # Target pose in the body frame
204 ee_target_pose_w = torch.zeros(scene.num_envs, 7, device=sim.device) # Target pose in the world frame (for marker)
205
206 # Set joint efforts to zero
207 zero_joint_efforts = torch.zeros(scene.num_envs, robot.num_joints, device=sim.device)
208 joint_efforts = torch.zeros(scene.num_envs, len(arm_joint_ids), device=sim.device)
209
210 count = 0
211 # Simulation loop
212 while simulation_app.is_running():
213 # reset every 500 steps
214 if count % 500 == 0:
215 # reset joint state to default
216 default_joint_pos = robot.data.default_joint_pos.clone()
217 default_joint_vel = robot.data.default_joint_vel.clone()
218 robot.write_joint_state_to_sim(default_joint_pos, default_joint_vel)
219 robot.set_joint_effort_target(zero_joint_efforts) # Set zero torques in the initial step
220 robot.write_data_to_sim()
221 robot.reset()
222 # reset contact sensor
223 contact_forces.reset()
224 # reset target pose
225 robot.update(sim_dt)
226 _, _, _, ee_pose_b, _, _, _, _, _, _ = update_states(
227 sim, scene, robot, ee_frame_idx, arm_joint_ids, contact_forces
228 ) # at reset, the jacobians are not updated to the latest state
229 command, ee_target_pose_b, ee_target_pose_w, current_goal_idx = update_target(
230 sim, scene, osc, root_pose_w, ee_target_set, current_goal_idx
231 )
232 # set the osc command
233 osc.reset()
234 command, task_frame_pose_b = convert_to_task_frame(osc, command=command, ee_target_pose_b=ee_target_pose_b)
235 osc.set_command(command=command, current_ee_pose_b=ee_pose_b, current_task_frame_pose_b=task_frame_pose_b)
236 else:
237 # get the updated states
238 (
239 jacobian_b,
240 mass_matrix,
241 gravity,
242 ee_pose_b,
243 ee_vel_b,
244 root_pose_w,
245 ee_pose_w,
246 ee_force_b,
247 joint_pos,
248 joint_vel,
249 ) = update_states(sim, scene, robot, ee_frame_idx, arm_joint_ids, contact_forces)
250 # compute the joint commands
251 joint_efforts = osc.compute(
252 jacobian_b=jacobian_b,
253 current_ee_pose_b=ee_pose_b,
254 current_ee_vel_b=ee_vel_b,
255 current_ee_force_b=ee_force_b,
256 mass_matrix=mass_matrix,
257 gravity=gravity,
258 current_joint_pos=joint_pos,
259 current_joint_vel=joint_vel,
260 nullspace_joint_pos_target=joint_centers,
261 )
262 # apply actions
263 robot.set_joint_effort_target(joint_efforts, joint_ids=arm_joint_ids)
264 robot.write_data_to_sim()
265
266 # update marker positions
267 ee_marker.visualize(ee_pose_w[:, 0:3], ee_pose_w[:, 3:7])
268 goal_marker.visualize(ee_target_pose_w[:, 0:3], ee_target_pose_w[:, 3:7])
269
270 # perform step
271 sim.step(render=True)
272 # update robot buffers
273 robot.update(sim_dt)
274 # update buffers
275 scene.update(sim_dt)
276 # update sim-time
277 count += 1
278
279
280# Update robot states
281def update_states(
282 sim: sim_utils.SimulationContext,
283 scene: InteractiveScene,
284 robot: Articulation,
285 ee_frame_idx: int,
286 arm_joint_ids: list[int],
287 contact_forces,
288):
289 """Update the robot states.
290
291 Args:
292 sim: (SimulationContext) Simulation context.
293 scene: (InteractiveScene) Interactive scene.
294 robot: (Articulation) Robot articulation.
295 ee_frame_idx: (int) End-effector frame index.
296 arm_joint_ids: (list[int]) Arm joint indices.
297 contact_forces: (ContactSensor) Contact sensor.
298
299 Returns:
300 jacobian_b (torch.tensor): Jacobian in the body frame.
301 mass_matrix (torch.tensor): Mass matrix.
302 gravity (torch.tensor): Gravity vector.
303 ee_pose_b (torch.tensor): End-effector pose in the body frame.
304 ee_vel_b (torch.tensor): End-effector velocity in the body frame.
305 root_pose_w (torch.tensor): Root pose in the world frame.
306 ee_pose_w (torch.tensor): End-effector pose in the world frame.
307 ee_force_b (torch.tensor): End-effector force in the body frame.
308 joint_pos (torch.tensor): The joint positions.
309 joint_vel (torch.tensor): The joint velocities.
310
311 Raises:
312 ValueError: Undefined target_type.
313 """
314 # obtain dynamics related quantities from simulation
315 ee_jacobi_idx = ee_frame_idx - 1
316 jacobian_w = robot.root_physx_view.get_jacobians()[:, ee_jacobi_idx, :, arm_joint_ids]
317 mass_matrix = robot.root_physx_view.get_generalized_mass_matrices()[:, arm_joint_ids, :][:, :, arm_joint_ids]
318 gravity = robot.root_physx_view.get_gravity_compensation_forces()[:, arm_joint_ids]
319 # Convert the Jacobian from world to root frame
320 jacobian_b = jacobian_w.clone()
321 root_rot_matrix = matrix_from_quat(quat_inv(robot.data.root_quat_w))
322 jacobian_b[:, :3, :] = torch.bmm(root_rot_matrix, jacobian_b[:, :3, :])
323 jacobian_b[:, 3:, :] = torch.bmm(root_rot_matrix, jacobian_b[:, 3:, :])
324
325 # Compute current pose of the end-effector
326 root_pos_w = robot.data.root_pos_w
327 root_quat_w = robot.data.root_quat_w
328 ee_pos_w = robot.data.body_pos_w[:, ee_frame_idx]
329 ee_quat_w = robot.data.body_quat_w[:, ee_frame_idx]
330 ee_pos_b, ee_quat_b = subtract_frame_transforms(root_pos_w, root_quat_w, ee_pos_w, ee_quat_w)
331 root_pose_w = torch.cat([root_pos_w, root_quat_w], dim=-1)
332 ee_pose_w = torch.cat([ee_pos_w, ee_quat_w], dim=-1)
333 ee_pose_b = torch.cat([ee_pos_b, ee_quat_b], dim=-1)
334
335 # Compute the current velocity of the end-effector
336 ee_vel_w = robot.data.body_vel_w[:, ee_frame_idx, :] # Extract end-effector velocity in the world frame
337 root_vel_w = robot.data.root_vel_w # Extract root velocity in the world frame
338 relative_vel_w = ee_vel_w - root_vel_w # Compute the relative velocity in the world frame
339 ee_lin_vel_b = quat_apply_inverse(robot.data.root_quat_w, relative_vel_w[:, 0:3]) # From world to root frame
340 ee_ang_vel_b = quat_apply_inverse(robot.data.root_quat_w, relative_vel_w[:, 3:6])
341 ee_vel_b = torch.cat([ee_lin_vel_b, ee_ang_vel_b], dim=-1)
342
343 # Calculate the contact force
344 ee_force_w = torch.zeros(scene.num_envs, 3, device=sim.device)
345 sim_dt = sim.get_physics_dt()
346 contact_forces.update(sim_dt) # update contact sensor
347 # Calculate the contact force by averaging over last four time steps (i.e., to smoothen) and
348 # taking the max of three surfaces as only one should be the contact of interest
349 ee_force_w, _ = torch.max(torch.mean(contact_forces.data.net_forces_w_history, dim=1), dim=1)
350
351 # This is a simplification, only for the sake of testing.
352 ee_force_b = ee_force_w
353
354 # Get joint positions and velocities
355 joint_pos = robot.data.joint_pos[:, arm_joint_ids]
356 joint_vel = robot.data.joint_vel[:, arm_joint_ids]
357
358 return (
359 jacobian_b,
360 mass_matrix,
361 gravity,
362 ee_pose_b,
363 ee_vel_b,
364 root_pose_w,
365 ee_pose_w,
366 ee_force_b,
367 joint_pos,
368 joint_vel,
369 )
370
371
372# Update the target commands
373def update_target(
374 sim: sim_utils.SimulationContext,
375 scene: InteractiveScene,
376 osc: OperationalSpaceController,
377 root_pose_w: torch.tensor,
378 ee_target_set: torch.tensor,
379 current_goal_idx: int,
380):
381 """Update the targets for the operational space controller.
382
383 Args:
384 sim: (SimulationContext) Simulation context.
385 scene: (InteractiveScene) Interactive scene.
386 osc: (OperationalSpaceController) Operational space controller.
387 root_pose_w: (torch.tensor) Root pose in the world frame.
388 ee_target_set: (torch.tensor) End-effector target set.
389 current_goal_idx: (int) Current goal index.
390
391 Returns:
392 command (torch.tensor): Updated target command.
393 ee_target_pose_b (torch.tensor): Updated target pose in the body frame.
394 ee_target_pose_w (torch.tensor): Updated target pose in the world frame.
395 next_goal_idx (int): Next goal index.
396
397 Raises:
398 ValueError: Undefined target_type.
399 """
400
401 # update the ee desired command
402 command = torch.zeros(scene.num_envs, osc.action_dim, device=sim.device)
403 command[:] = ee_target_set[current_goal_idx]
404
405 # update the ee desired pose
406 ee_target_pose_b = torch.zeros(scene.num_envs, 7, device=sim.device)
407 for target_type in osc.cfg.target_types:
408 if target_type == "pose_abs":
409 ee_target_pose_b[:] = command[:, :7]
410 elif target_type == "wrench_abs":
411 pass # ee_target_pose_b could stay at the root frame for force control, what matters is ee_target_b
412 else:
413 raise ValueError("Undefined target_type within update_target().")
414
415 # update the target desired pose in world frame (for marker)
416 ee_target_pos_w, ee_target_quat_w = combine_frame_transforms(
417 root_pose_w[:, 0:3], root_pose_w[:, 3:7], ee_target_pose_b[:, 0:3], ee_target_pose_b[:, 3:7]
418 )
419 ee_target_pose_w = torch.cat([ee_target_pos_w, ee_target_quat_w], dim=-1)
420
421 next_goal_idx = (current_goal_idx + 1) % len(ee_target_set)
422
423 return command, ee_target_pose_b, ee_target_pose_w, next_goal_idx
424
425
426# Convert the target commands to the task frame
427def convert_to_task_frame(osc: OperationalSpaceController, command: torch.tensor, ee_target_pose_b: torch.tensor):
428 """Converts the target commands to the task frame.
429
430 Args:
431 osc: OperationalSpaceController object.
432 command: Command to be converted.
433 ee_target_pose_b: Target pose in the body frame.
434
435 Returns:
436 command (torch.tensor): Target command in the task frame.
437 task_frame_pose_b (torch.tensor): Target pose in the task frame.
438
439 Raises:
440 ValueError: Undefined target_type.
441 """
442 command = command.clone()
443 task_frame_pose_b = ee_target_pose_b.clone()
444
445 cmd_idx = 0
446 for target_type in osc.cfg.target_types:
447 if target_type == "pose_abs":
448 command[:, :3], command[:, 3:7] = subtract_frame_transforms(
449 task_frame_pose_b[:, :3], task_frame_pose_b[:, 3:], command[:, :3], command[:, 3:7]
450 )
451 cmd_idx += 7
452 elif target_type == "wrench_abs":
453 # These are already defined in target frame for ee_goal_wrench_set_tilted_task (since it is
454 # easier), so not transforming
455 cmd_idx += 6
456 else:
457 raise ValueError("Undefined target_type within _convert_to_task_frame().")
458
459 return command, task_frame_pose_b
460
461
462def main():
463 """Main function."""
464 # Load kit helper
465 sim_cfg = sim_utils.SimulationCfg(dt=0.01, device=args_cli.device)
466 sim = sim_utils.SimulationContext(sim_cfg)
467 # Set main camera
468 sim.set_camera_view([2.5, 2.5, 2.5], [0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
469 # Design scene
470 scene_cfg = SceneCfg(num_envs=args_cli.num_envs, env_spacing=2.0)
471 scene = InteractiveScene(scene_cfg)
472 # Play the simulator
473 sim.reset()
474 # Now we are ready!
475 print("[INFO]: Setup complete...")
476 # Run the simulator
477 run_simulator(sim, scene)
478
479
480if __name__ == "__main__":
481 # run the main function
482 main()
483 # close sim app
484 simulation_app.close()
创建一个操作空间控制器#
OperationalSpaceController 类计算机器人在任务空间中同时进行运动和力控制时的关节力/扭矩。
这个任务空间的参考坐标系可以是欧几里德空间中的任意坐标系。默认情况下,它是机器人的基坐标系。然而,在某些情况下,相对于其他坐标系定义目标坐标会更容易。在这种情况下,应该在 set_command 方法的 current_task_frame_pose_b 参数中提供该任务参考坐标系相对于机器人基坐标系的姿态。例如,在这个教程中,将目标命令相对于与墙面平行的坐标系定义是有意义的,因为这样力控制方向将仅在该坐标系的z轴上非零。设置为具有与墙面相同方向的目标姿态就是这样一个候选项,并在本教程中作为任务坐标系使用。因此,应该以这个任务参考坐标系为考虑来设置所有到 OperationalSpaceControllerCfg 的参数。
对于运动控制,任务空间目标可以被设定为绝对(即,相对于机器人基坐标系定义, target_types: "pose_abs") 或相对于末端执行器当前姿态(即, target_types: "pose_rel") 。对于力控制,任务空间目标可以被设定为绝对(即,相对于机器人基坐标系定义, target_types: "force_abs") 。如果希望同时应用姿态和力控制, target_types 应该是一个列表,如 ["pose_abs", "wrench_abs"] 或 ["pose_rel", "wrench_abs"] 。
运动和力控制将应用的轴可以使用 motion_control_axes_task 和 force_control_axes_task 参数进行指定。这些列表应包含所有六个轴(位置和旋转)的0/1,并且彼此互补(例如,对于x轴,如果 motion_control_axes_task 为 0 ,则 force_control_axes_task 应为 1 )。
对于运动控制轴,可以使用 motion_control_stiffness 和 motion_damping_ratio_task 参数指定所需的刚度和阻尼比值,这可以是一个标量(所有轴的相同值)或一个包含六个标量的列表,每个值对应一个轴。如果需要,刚度和阻尼比值可以作为命令参数(例如,使用RL学习这些值或在运行时更改这些值)。为此, impedance_mode 应为 "variable_kp" 以在命令中包含刚度值,或者为 "variable" 以在命令中同时包含刚度和阻尼比值。在这些情况下,还应设置 motion_stiffness_limits_task 和 motion_damping_limits_task ,这会限制刚度和阻尼比值的范围。
对于接触力控制,可以通过不设置 contact_wrench_stiffness_task 来应用开环力控制,或者通过设置所需刚度值来应用带有前馈项的闭环力控制,其使用 contact_wrench_stiffness_task 参数,该参数可以是一个标量或六个标量的列表。请注意,目前只有接触力矩的线性部分(因此是 contact_wrench_stiffness_task 的前三个元素)在闭环控制中被考虑,因为接触传感器无法测量旋转部分。
对于运动控制,应将 inertial_dynamics_decoupling 设置为 True ,以使用机器人的惯性矩阵来解耦任务空间中的期望加速度。这对于运动控制的精确性非常重要,特别是对于快速运动。这种惯性解耦考虑了所有六个运动轴之间的耦合。如果需要,可以通过将 partial_inertial_dynamics_decoupling 设置为 True 来忽略平移和旋转轴之间的惯性耦合。
如果希望在操作空间指令中包含重力补偿,则应将 gravity_compensation 设置为 True 。
关于操作空间控制的一个最终考虑是如何处理冗余机器人运动学中的零空间。零空间是关节空间的子空间,它不会影响任务空间坐标。如果没有采取措施来控制零空间,机器人关节将会浮动而不移动末端执行器。这可能是不可取的(例如,机器人关节可能会接近它们的极限),因此可能希望在零空间内控制机器人的行为。一个方法是将 nullspace_control 设置为 "position" (默认值为 "none" ),这将集成一个零空间 PD 控制器,将机器人关节吸引到期望目标,而不影响任务空间。此零空间控制器的行为可以通过 nullspace_stiffness 和 nullspace_damping_ratio 参数来定义。请注意,零空间和任务空间加速度的理论解耦只有在 inertial_dynamics_decoupling 设置为 True 且 partial_inertial_dynamics_decoupling 设置为 False 时才可能。
包含的 OSC 实现以批处理格式进行计算,并使用 PyTorch 操作。
在本教程中,我们将使用 "pose_abs" 控制除 z 轴以外的所有轴的运动,使用 "wrench_abs" 控制 z 轴上的力。此外,我们将在运动控制中包括完整的惯性解耦,并且不包括重力补偿,因为机器人配置中禁用了重力。我们将将阻抗模式设置为 "variable_kp" ,以动态更改刚度值( motion_damping_ratio_task 设置为 1:kd 值会根据 kp 值自适应以保持过阻尼响应)。最后,将 nullspace_control 设置为使用 "position" ,其中关节设定点被设置为关节位置限制的中心。
# Create the OSC
osc_cfg = OperationalSpaceControllerCfg(
target_types=["pose_abs", "wrench_abs"],
impedance_mode="variable_kp",
inertial_dynamics_decoupling=True,
partial_inertial_dynamics_decoupling=False,
gravity_compensation=False,
motion_damping_ratio_task=1.0,
contact_wrench_stiffness_task=[0.0, 0.0, 0.1, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
motion_control_axes_task=[1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1],
contact_wrench_control_axes_task=[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
nullspace_control="position",
)
osc = OperationalSpaceController(osc_cfg, num_envs=scene.num_envs, device=sim.device)
更新机器人的状态#
OSC 实现是一个纯计算类。因此,它期望用户提供有关机器人的必要信息。这包括机器人的雅可比矩阵、质量/惯性矩阵、末端执行器姿态、速度和接触力,均在根坐标系中,最后是关节位置和速度。此外,如果需要,用户应提供重力补偿矢量和零空间关节位置目标。
# Update robot states
def update_states(
sim: sim_utils.SimulationContext,
scene: InteractiveScene,
robot: Articulation,
ee_frame_idx: int,
arm_joint_ids: list[int],
contact_forces,
):
"""Update the robot states.
Args:
sim: (SimulationContext) Simulation context.
scene: (InteractiveScene) Interactive scene.
robot: (Articulation) Robot articulation.
ee_frame_idx: (int) End-effector frame index.
arm_joint_ids: (list[int]) Arm joint indices.
contact_forces: (ContactSensor) Contact sensor.
Returns:
jacobian_b (torch.tensor): Jacobian in the body frame.
mass_matrix (torch.tensor): Mass matrix.
gravity (torch.tensor): Gravity vector.
ee_pose_b (torch.tensor): End-effector pose in the body frame.
ee_vel_b (torch.tensor): End-effector velocity in the body frame.
root_pose_w (torch.tensor): Root pose in the world frame.
ee_pose_w (torch.tensor): End-effector pose in the world frame.
ee_force_b (torch.tensor): End-effector force in the body frame.
joint_pos (torch.tensor): The joint positions.
joint_vel (torch.tensor): The joint velocities.
Raises:
ValueError: Undefined target_type.
"""
# obtain dynamics related quantities from simulation
ee_jacobi_idx = ee_frame_idx - 1
jacobian_w = robot.root_physx_view.get_jacobians()[:, ee_jacobi_idx, :, arm_joint_ids]
mass_matrix = robot.root_physx_view.get_generalized_mass_matrices()[:, arm_joint_ids, :][:, :, arm_joint_ids]
gravity = robot.root_physx_view.get_gravity_compensation_forces()[:, arm_joint_ids]
# Convert the Jacobian from world to root frame
jacobian_b = jacobian_w.clone()
root_rot_matrix = matrix_from_quat(quat_inv(robot.data.root_quat_w))
jacobian_b[:, :3, :] = torch.bmm(root_rot_matrix, jacobian_b[:, :3, :])
jacobian_b[:, 3:, :] = torch.bmm(root_rot_matrix, jacobian_b[:, 3:, :])
# Compute current pose of the end-effector
root_pos_w = robot.data.root_pos_w
root_quat_w = robot.data.root_quat_w
ee_pos_w = robot.data.body_pos_w[:, ee_frame_idx]
ee_quat_w = robot.data.body_quat_w[:, ee_frame_idx]
ee_pos_b, ee_quat_b = subtract_frame_transforms(root_pos_w, root_quat_w, ee_pos_w, ee_quat_w)
root_pose_w = torch.cat([root_pos_w, root_quat_w], dim=-1)
ee_pose_w = torch.cat([ee_pos_w, ee_quat_w], dim=-1)
ee_pose_b = torch.cat([ee_pos_b, ee_quat_b], dim=-1)
# Compute the current velocity of the end-effector
ee_vel_w = robot.data.body_vel_w[:, ee_frame_idx, :] # Extract end-effector velocity in the world frame
root_vel_w = robot.data.root_vel_w # Extract root velocity in the world frame
relative_vel_w = ee_vel_w - root_vel_w # Compute the relative velocity in the world frame
ee_lin_vel_b = quat_apply_inverse(robot.data.root_quat_w, relative_vel_w[:, 0:3]) # From world to root frame
ee_ang_vel_b = quat_apply_inverse(robot.data.root_quat_w, relative_vel_w[:, 3:6])
ee_vel_b = torch.cat([ee_lin_vel_b, ee_ang_vel_b], dim=-1)
# Calculate the contact force
ee_force_w = torch.zeros(scene.num_envs, 3, device=sim.device)
sim_dt = sim.get_physics_dt()
contact_forces.update(sim_dt) # update contact sensor
# Calculate the contact force by averaging over last four time steps (i.e., to smoothen) and
# taking the max of three surfaces as only one should be the contact of interest
ee_force_w, _ = torch.max(torch.mean(contact_forces.data.net_forces_w_history, dim=1), dim=1)
# This is a simplification, only for the sake of testing.
ee_force_b = ee_force_w
# Get joint positions and velocities
joint_pos = robot.data.joint_pos[:, arm_joint_ids]
joint_vel = robot.data.joint_vel[:, arm_joint_ids]
return (
jacobian_b,
mass_matrix,
gravity,
ee_pose_b,
ee_vel_b,
root_pose_w,
ee_pose_w,
ee_force_b,
joint_pos,
joint_vel,
)
计算机器人命令#
OSC 分离了设定期望命令和计算期望关节位置的操作。要设定期望命令,用户应提供命令向量,其中包括目标命令(即在 OSC 配置的 target_types 参数中出现的顺序)以及如果 impedance_mode 设置为 "variable_kp" 或 "variable" 时的期望刚度和阻尼比值。它们应该都在与任务框架相同的坐标系中(例如,用 _task 下标表示)并连接在一起。
在本教程中,期望的力矩已经相对于任务框架进行了定义,并且期望的姿势被转换到任务框架中,如下所示:
# Convert the target commands to the task frame
def convert_to_task_frame(osc: OperationalSpaceController, command: torch.tensor, ee_target_pose_b: torch.tensor):
"""Converts the target commands to the task frame.
Args:
osc: OperationalSpaceController object.
command: Command to be converted.
ee_target_pose_b: Target pose in the body frame.
Returns:
command (torch.tensor): Target command in the task frame.
task_frame_pose_b (torch.tensor): Target pose in the task frame.
Raises:
ValueError: Undefined target_type.
"""
command = command.clone()
task_frame_pose_b = ee_target_pose_b.clone()
cmd_idx = 0
for target_type in osc.cfg.target_types:
if target_type == "pose_abs":
command[:, :3], command[:, 3:7] = subtract_frame_transforms(
task_frame_pose_b[:, :3], task_frame_pose_b[:, 3:], command[:, :3], command[:, 3:7]
)
cmd_idx += 7
elif target_type == "wrench_abs":
# These are already defined in target frame for ee_goal_wrench_set_tilted_task (since it is
# easier), so not transforming
cmd_idx += 6
else:
raise ValueError("Undefined target_type within _convert_to_task_frame().")
return command, task_frame_pose_b
OSC 命令是使用任务坐标系中的命令向量设置的,基坐标系中的末端执行器姿势和基坐标系中的任务(参考)坐标系姿势如下。这些信息是必要的,因为内部计算是在基坐标系中完成的。
# set the osc command
osc.reset()
command, task_frame_pose_b = convert_to_task_frame(osc, command=command, ee_target_pose_b=ee_target_pose_b)
osc.set_command(command=command, current_ee_pose_b=ee_pose_b, current_task_frame_pose_b=task_frame_pose_b)
使用提供的机器人状态和所需命令计算关节力/扭矩值,如下所示:
# compute the joint commands
joint_efforts = osc.compute(
jacobian_b=jacobian_b,
current_ee_pose_b=ee_pose_b,
current_ee_vel_b=ee_vel_b,
current_ee_force_b=ee_force_b,
mass_matrix=mass_matrix,
gravity=gravity,
current_joint_pos=joint_pos,
current_joint_vel=joint_vel,
nullspace_joint_pos_target=joint_centers,
)
计算得出的关节努力/力矩目标随后可以应用于机器人中。
# apply actions
robot.set_joint_effort_target(joint_efforts, joint_ids=arm_joint_ids)
robot.write_data_to_sim()
代码执行#
你现在可以运行脚本并查看结果:
./isaaclab.sh -p scripts/tutorials/05_controllers/run_osc.py --num_envs 128
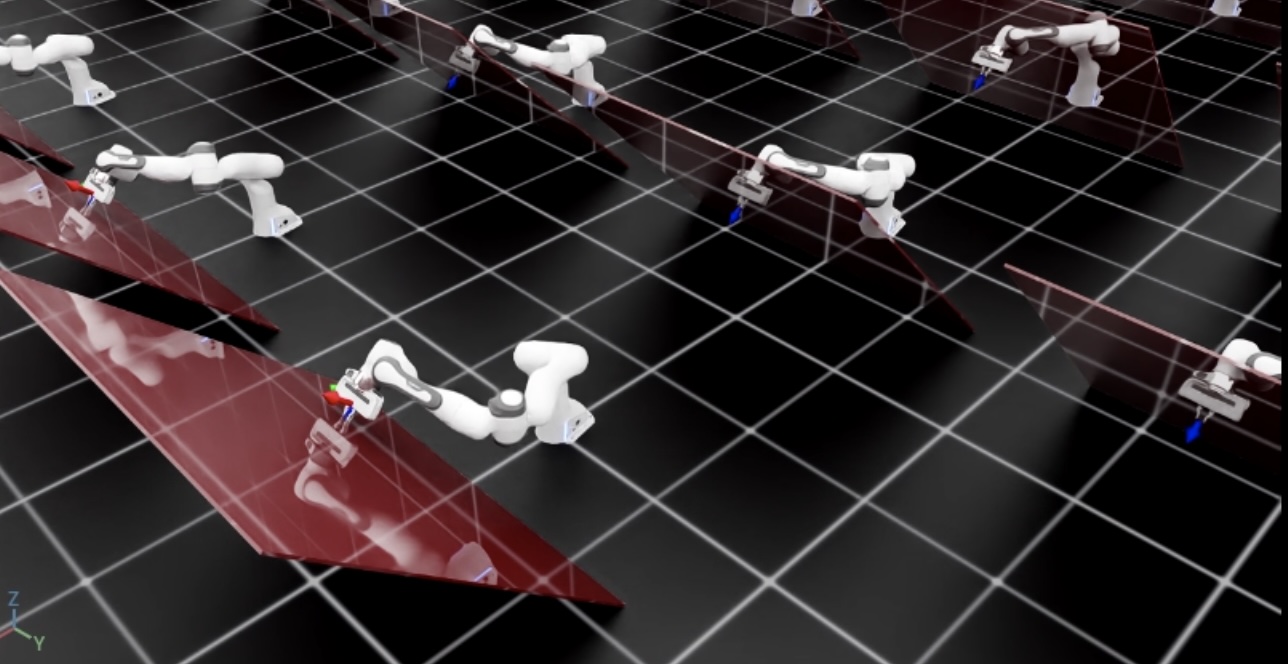
该脚本将启动一个包含128个机器人的仿真。将使用OSC进行机器人的控制。当前和期望的末端执行器姿势应该使用框架标记显示,除了红色倾斜墙之外。您应该看到机器人在施加垂直于墙面的恒定力的同时到达期望姿势。
要停止仿真,您可以关闭窗口或在终端中按 Ctrl+C 。
