坐标系转换器#
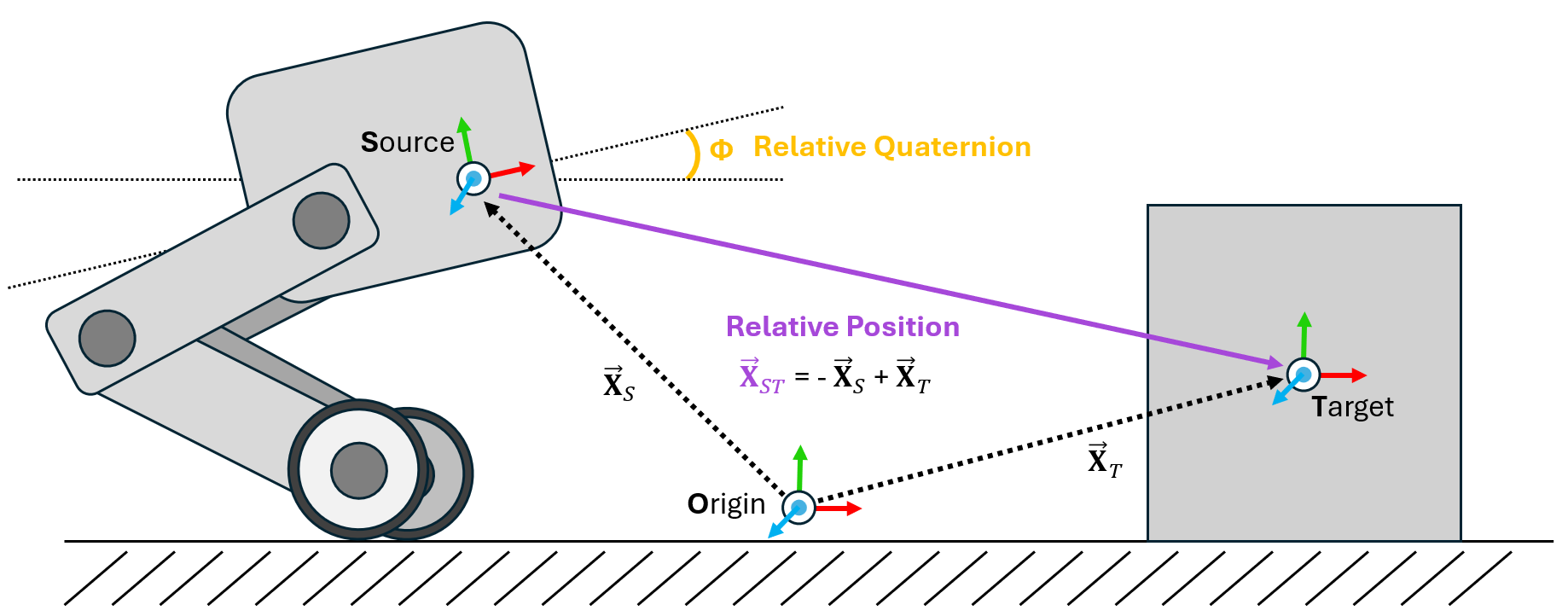
在物理仿真中,最常见的操作之一是坐标系转换:在任意欧几里得坐标系的基底下重写向量或四元数。虽然在 Isaac 和 USD 中有多种方法可以实现这一操作,但在 Isaac Lab 的基于 GPU 的仿真和克隆环境中实现这些方法可能会显得繁琐。为了解决这个问题,我们设计了 坐标系转换传感器,它能够跟踪并计算场景中感兴趣的刚体的相对坐标系转换。
传感器的最小定义由一个源坐标系和一个目标坐标系列表组成。这些定义分别以基本路径(用于源)和支持正则表达式的基本路径列表(用于跟踪的刚体的目标)表示。
@configclass
class FrameTransformerSensorSceneCfg(InteractiveSceneCfg):
"""Design the scene with sensors on the robot."""
# ground plane
ground = AssetBaseCfg(prim_path="/World/defaultGroundPlane", spawn=sim_utils.GroundPlaneCfg())
# lights
dome_light = AssetBaseCfg(
prim_path="/World/Light", spawn=sim_utils.DomeLightCfg(intensity=3000.0, color=(0.75, 0.75, 0.75))
)
# robot
robot = ANYMAL_C_CFG.replace(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot")
# Rigid Object
cube = RigidObjectCfg(
prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Cube",
spawn=sim_utils.CuboidCfg(
size=(1,1,1),
rigid_props=sim_utils.RigidBodyPropertiesCfg(),
mass_props=sim_utils.MassPropertiesCfg(mass=100.0),
collision_props=sim_utils.CollisionPropertiesCfg(),
physics_material=sim_utils.RigidBodyMaterialCfg(static_friction=1.0),
visual_material=sim_utils.PreviewSurfaceCfg(diffuse_color=(0.0, 1.0, 0.0), metallic=0.2),
),
init_state=RigidObjectCfg.InitialStateCfg(pos=(5, 0, 0.5)),
)
specific_transforms = FrameTransformerCfg(
prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/base",
target_frames=[
FrameTransformerCfg.FrameCfg(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/LF_FOOT"),
FrameTransformerCfg.FrameCfg(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/RF_FOOT"),
],
debug_vis=True,
)
cube_transform = FrameTransformerCfg(
prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/base",
target_frames=[
FrameTransformerCfg.FrameCfg(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Cube")
],
debug_vis=False,
)
robot_transforms = FrameTransformerCfg(
prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/base",
target_frames=[
FrameTransformerCfg.FrameCfg(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/.*")
],
debug_vis=False,
)
我们现在可以运行场景并查询传感器以获取数据
def run_simulator(sim: sim_utils.SimulationContext, scene: InteractiveScene):
.
.
.
# Simulate physics
while simulation_app.is_running():
.
.
.
# print information from the sensors
print("-------------------------------")
print(scene["specific_transforms"])
print("relative transforms:", scene["specific_transforms"].data.target_pos_source)
print("relative orientations:", scene["specific_transforms"].data.target_quat_source)
print("-------------------------------")
print(scene["cube_transform"])
print("relative transform:", scene["cube_transform"].data.target_pos_source)
print("-------------------------------")
print(scene["robot_transforms"])
print("relative transforms:", scene["robot_transforms"].data.target_pos_source)
让我们来看看跟踪特定物体的结果。首先,我们可以查看来自脚部传感器的数据。
-------------------------------
FrameTransformer @ '/World/envs/env_.*/Robot/base':
tracked body frames: ['base', 'LF_FOOT', 'RF_FOOT']
number of envs: 1
source body frame: base
target frames (count: ['LF_FOOT', 'RF_FOOT']): 2
relative transforms: tensor([[[ 0.4658, 0.3085, -0.4840],
[ 0.4487, -0.2959, -0.4828]]], device='cuda:0')
relative orientations: tensor([[[ 0.9623, 0.0072, -0.2717, -0.0020],
[ 0.9639, 0.0052, -0.2663, -0.0014]]], device='cuda:0')
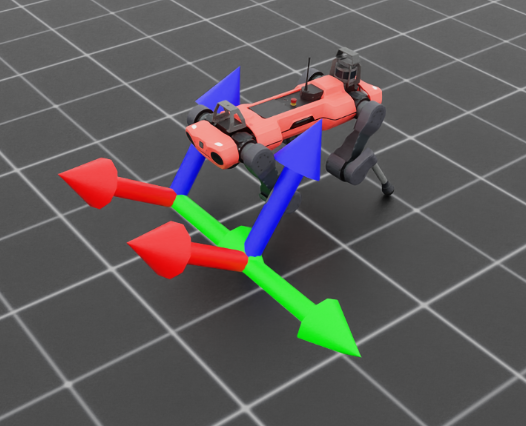
通过激活可视化工具,我们可以看到脚部的坐标系略微 “向上” 旋转。我们还可以通过查询传感器数据来查看明确的相对位置和旋转,这些数据以与跟踪坐标系相同顺序的列表形式返回。如果我们检查由正则表达式指定的变换,这一点变得更加明显。
-------------------------------
FrameTransformer @ '/World/envs/env_.*/Robot/base':
tracked body frames: ['base', 'LF_FOOT', 'LF_HIP', 'LF_SHANK', 'LF_THIGH', 'LH_FOOT', 'LH_HIP', 'LH_SHANK', 'LH_THIGH', 'RF_FOOT', 'RF_HIP', 'RF_SHANK', 'RF_THIGH', 'RH_FOOT', 'RH_HIP', 'RH_SHANK', 'RH_THIGH', 'base']
number of envs: 1
source body frame: base
target frames (count: ['LF_FOOT', 'LF_HIP', 'LF_SHANK', 'LF_THIGH', 'LH_FOOT', 'LH_HIP', 'LH_SHANK', 'LH_THIGH', 'RF_FOOT', 'RF_HIP', 'RF_SHANK', 'RF_THIGH', 'RH_FOOT', 'RH_HIP', 'RH_SHANK', 'RH_THIGH', 'base']): 17
relative transforms: tensor([[[ 4.6581e-01, 3.0846e-01, -4.8398e-01],
[ 2.9990e-01, 1.0400e-01, -1.7062e-09],
[ 2.1409e-01, 2.9177e-01, -2.4214e-01],
[ 3.5980e-01, 1.8780e-01, 1.2608e-03],
[-4.8813e-01, 3.0973e-01, -4.5927e-01],
[-2.9990e-01, 1.0400e-01, 2.7044e-09],
[-2.1495e-01, 2.9264e-01, -2.4198e-01],
[-3.5980e-01, 1.8780e-01, 1.5582e-03],
[ 4.4871e-01, -2.9593e-01, -4.8277e-01],
[ 2.9990e-01, -1.0400e-01, -2.7057e-09],
[ 1.9971e-01, -2.8554e-01, -2.3778e-01],
[ 3.5980e-01, -1.8781e-01, -9.1049e-04],
[-5.0090e-01, -2.9095e-01, -4.5746e-01],
[-2.9990e-01, -1.0400e-01, 6.3592e-09],
[-2.1860e-01, -2.8251e-01, -2.5163e-01],
[-3.5980e-01, -1.8779e-01, -1.8792e-03],
[ 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00]]], device='cuda:0')
在这里,传感器正在跟踪 Robot/base 的所有刚体子节点,但这个表达式是 包含的 ,意味着源身体本身也是一个目标。这可以通过检查源和目标列表来看,base 出现了两次,也可以通过返回的数据看出,传感器返回相对于自身的变换(0, 0, 0)。
frame_transformer_sensor.py 的代码
1# Copyright (c) 2022-2025, The Isaac Lab Project Developers.
2# All rights reserved.
3#
4# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
5
6import argparse
7
8from omni.isaac.lab.app import AppLauncher
9
10# add argparse arguments
11parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Tutorial on adding sensors on a robot.")
12parser.add_argument("--num_envs", type=int, default=1, help="Number of environments to spawn.")
13# append AppLauncher cli args
14AppLauncher.add_app_launcher_args(parser)
15# parse the arguments
16args_cli = parser.parse_args()
17
18# launch omniverse app
19app_launcher = AppLauncher(args_cli)
20simulation_app = app_launcher.app
21
22"""Rest everything follows."""
23
24import torch
25
26import omni.isaac.lab.sim as sim_utils
27from omni.isaac.lab.assets import AssetBaseCfg, RigidObjectCfg
28from omni.isaac.lab.scene import InteractiveScene, InteractiveSceneCfg
29from omni.isaac.lab.sensors import FrameTransformerCfg
30from omni.isaac.lab.utils import configclass
31
32##
33# Pre-defined configs
34##
35from omni.isaac.lab_assets.anymal import ANYMAL_C_CFG # isort: skip
36
37
38@configclass
39class FrameTransformerSensorSceneCfg(InteractiveSceneCfg):
40 """Design the scene with sensors on the robot."""
41
42 # ground plane
43 ground = AssetBaseCfg(prim_path="/World/defaultGroundPlane", spawn=sim_utils.GroundPlaneCfg())
44
45 # lights
46 dome_light = AssetBaseCfg(
47 prim_path="/World/Light", spawn=sim_utils.DomeLightCfg(intensity=3000.0, color=(0.75, 0.75, 0.75))
48 )
49
50 # robot
51 robot = ANYMAL_C_CFG.replace(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot")
52
53 # Rigid Object
54 cube = RigidObjectCfg(
55 prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Cube",
56 spawn=sim_utils.CuboidCfg(
57 size=(1, 1, 1),
58 rigid_props=sim_utils.RigidBodyPropertiesCfg(),
59 mass_props=sim_utils.MassPropertiesCfg(mass=100.0),
60 collision_props=sim_utils.CollisionPropertiesCfg(),
61 physics_material=sim_utils.RigidBodyMaterialCfg(static_friction=1.0),
62 visual_material=sim_utils.PreviewSurfaceCfg(diffuse_color=(0.0, 1.0, 0.0), metallic=0.2),
63 ),
64 init_state=RigidObjectCfg.InitialStateCfg(pos=(5, 0, 0.5)),
65 )
66
67 specific_transforms = FrameTransformerCfg(
68 prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/base",
69 target_frames=[
70 FrameTransformerCfg.FrameCfg(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/LF_FOOT"),
71 FrameTransformerCfg.FrameCfg(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/RF_FOOT"),
72 ],
73 debug_vis=True,
74 )
75
76 cube_transform = FrameTransformerCfg(
77 prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/base",
78 target_frames=[FrameTransformerCfg.FrameCfg(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Cube")],
79 debug_vis=False,
80 )
81
82 robot_transforms = FrameTransformerCfg(
83 prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/base",
84 target_frames=[FrameTransformerCfg.FrameCfg(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/.*")],
85 debug_vis=False,
86 )
87
88
89def run_simulator(sim: sim_utils.SimulationContext, scene: InteractiveScene):
90 """Run the simulator."""
91 # Define simulation stepping
92 sim_dt = sim.get_physics_dt()
93 sim_time = 0.0
94 count = 0
95
96 # Simulate physics
97 while simulation_app.is_running():
98
99 if count % 500 == 0:
100 # reset counter
101 count = 0
102 # reset the scene entities
103 # root state
104 # we offset the root state by the origin since the states are written in simulation world frame
105 # if this is not done, then the robots will be spawned at the (0, 0, 0) of the simulation world
106 root_state = scene["robot"].data.default_root_state.clone()
107 root_state[:, :3] += scene.env_origins
108 scene["robot"].write_root_link_pose_to_sim(root_state[:, :7])
109 scene["robot"].write_root_com_velocity_to_sim(root_state[:, 7:])
110 # set joint positions with some noise
111 joint_pos, joint_vel = (
112 scene["robot"].data.default_joint_pos.clone(),
113 scene["robot"].data.default_joint_vel.clone(),
114 )
115 joint_pos += torch.rand_like(joint_pos) * 0.1
116 scene["robot"].write_joint_state_to_sim(joint_pos, joint_vel)
117 # clear internal buffers
118 scene.reset()
119 print("[INFO]: Resetting robot state...")
120 # Apply default actions to the robot
121 # -- generate actions/commands
122 targets = scene["robot"].data.default_joint_pos
123 # -- apply action to the robot
124 scene["robot"].set_joint_position_target(targets)
125 # -- write data to sim
126 scene.write_data_to_sim()
127 # perform step
128 sim.step()
129 # update sim-time
130 sim_time += sim_dt
131 count += 1
132 # update buffers
133 scene.update(sim_dt)
134
135 # print information from the sensors
136 print("-------------------------------")
137 print(scene["specific_transforms"])
138 print("relative transforms:", scene["specific_transforms"].data.target_pos_source)
139 print("relative orientations:", scene["specific_transforms"].data.target_quat_source)
140 print("-------------------------------")
141 print(scene["cube_transform"])
142 print("relative transform:", scene["cube_transform"].data.target_pos_source)
143 print("-------------------------------")
144 print(scene["robot_transforms"])
145 print("relative transforms:", scene["robot_transforms"].data.target_pos_source)
146
147
148def main():
149 """Main function."""
150
151 # Initialize the simulation context
152 sim_cfg = sim_utils.SimulationCfg(dt=0.005, device=args_cli.device)
153 sim = sim_utils.SimulationContext(sim_cfg)
154 # Set main camera
155 sim.set_camera_view(eye=[3.5, 3.5, 3.5], target=[0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
156 # design scene
157 scene_cfg = FrameTransformerSensorSceneCfg(num_envs=args_cli.num_envs, env_spacing=2.0)
158 scene = InteractiveScene(scene_cfg)
159 # Play the simulator
160 sim.reset()
161 # Now we are ready!
162 print("[INFO]: Setup complete...")
163 # Run the simulator
164 run_simulator(sim, scene)
165
166
167if __name__ == "__main__":
168 # run the main function
169 main()
170 # close sim app
171 simulation_app.close()

