SkillGen for Automated Demonstration Generation#
SkillGen is an advanced demonstration generation system that enhances Isaac Lab Mimic by integrating motion planning. It generates high-quality, adaptive, collision-free robot demonstrations by combining human-provided subtask segments with automated motion planning.
What is SkillGen?#
SkillGen addresses key limitations in traditional demonstration generation:
Motion Quality: Uses cuRobo’s GPU-accelerated motion planner to generate smooth, collision-free trajectories
Validity: Generates kinematically feasible plans between skill segments
Diversity: Generates varied demonstrations through configurable sampling and planning parameters
Adaptability: Generates demonstrations that can be adapted to new object placements and scene configurations during data generation
The system works by taking manually annotated human demonstrations, extracting localized subtask skills (see Subtasks in SkillGen), and using cuRobo to plan feasible motions between these skill segments while respecting robot kinematics and collision constraints.
Prerequisites#
Before using SkillGen, you must understand:
Teleoperation: How to control robots and record demonstrations using keyboard, SpaceMouse, or hand tracking
Isaac Lab Mimic: The complete workflow including data collection, annotation, generation, and policy training
Important
Review the Teleoperation and Imitation Learning with Isaac Lab Mimic documentation thoroughly before proceeding with SkillGen.
Installation#
SkillGen requires Isaac Lab, Isaac Sim, and cuRobo. Follow these steps in your Isaac Lab conda environment.
Step 1: Install and verify Isaac Sim and Isaac Lab#
Follow the official Isaac Sim and Isaac Lab installation guide here.
Step 2: Install cuRobo#
cuRobo provides the motion planning capabilities for SkillGen. This installation is tested to work with Isaac Lab’s PyTorch and CUDA requirements:
# One line installation of cuRobo (formatted for readability)
conda install -c nvidia cuda-toolkit=12.8 -y && \
export CUDA_HOME="$CONDA_PREFIX" && \
export PATH="$CUDA_HOME/bin:$PATH" && \
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="$CUDA_HOME/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH" && \
export TORCH_CUDA_ARCH_LIST="8.0+PTX" && \
pip install -e "git+https://github.com/NVlabs/curobo.git@ebb71702f3f70e767f40fd8e050674af0288abe8#egg=nvidia-curobo" --no-build-isolation
Note
The commit hash
ebb71702f3f70e767f40fd8e050674af0288abe8is tested with Isaac Lab - using other versions may cause compatibility issues. This commit has the support for quad face mesh triangulation, required for cuRobo to parse usds as collision objects.cuRobo is installed from source and is editable installed. This means that the cuRobo source code will be cloned in the current directory under
src/nvidia-curobo. Users can choose their working directory to install cuRobo.TORCH_CUDA_ARCH_LISTin the above command should match your GPU’s CUDA compute capability (e.g.,8.0for A100,8.6for many RTX 30‑series,8.9for RTX 4090); the+PTXsuffix embeds PTX for forward compatibility so newer GPUs can JIT‑compile when native SASS isn’t included.
Warning
cuRobo installation may fail if Isaac Sim environment scripts are sourced
Sourcing Omniverse Kit/Isaac Sim environment scripts (for example, setup_conda_env.sh) exports PYTHONHOME and PYTHONPATH to the Kit runtime and its pre-bundled Python packages. During cuRobo installation this can cause conda to import Omniverse’s bundled libraries (e.g., requests/urllib3) before initialization, resulting in a crash (often seen as a TypeError referencing omni.kit.pip_archive).
Do one of the following:
Install cuRobo from a clean shell that has not sourced any Omniverse/Isaac Sim scripts.
Temporarily reset or ignore inherited Python environment variables (notably
PYTHONPATHandPYTHONHOME) before invoking Conda, so Kit’s Python does not shadow your Conda environment.Use Conda mechanisms that do not rely on shell activation and avoid inheriting the current shell’s Python variables.
After installation completes, you may source Isaac Lab/Isaac Sim scripts again for normal use.
Step 3: Install Rerun#
For trajectory visualization during development:
pip install rerun-sdk==0.23
Note
Rerun Visualization Setup:
Rerun is optional but highly recommended for debugging and validating planned trajectories during development
Enable trajectory visualization by setting
visualize_plan = Truein the cuRobo planner configurationWhen enabled, cuRobo planner interface will stream planned end-effector trajectories, waypoints, and collision data to Rerun for interactive inspection
Visualization helps identify planning issues, collision problems, and trajectory smoothness before full dataset generation
Can also be ran with
--headlessto disable isaacsim visualization but still visualize and debug end effector trajectories
Step 4: Verify Installation#
Test that cuRobo works with Isaac Lab:
# This should run without import errors
python -c "import curobo; print('cuRobo installed successfully')"
Tip
If you run into libstdc++.so.6: version 'GLIBCXX_3.4.30' not found error, you can try these commands to fix it:
conda config --env --set channel_priority strict
conda config --env --add channels conda-forge
conda install -y -c conda-forge "libstdcxx-ng>=12" "libgcc-ng>=12"
Download the SkillGen Dataset#
We provide a pre-annotated dataset to help you get started quickly with SkillGen.
Dataset Contents#
The dataset contains:
Human demonstrations of Franka arm cube stacking
Manually annotated subtask boundaries for each demonstration
Compatible with both basic cube stacking and adaptive bin cube stacking tasks
Download and Setup#
Download the pre-annotated dataset by clicking here.
Prepare the datasets directory and move the downloaded file:
# Make sure you are in the root directory of your Isaac Lab workspace
cd /path/to/your/IsaacLab
# Create the datasets directory if it does not exist
mkdir -p datasets
# Move the downloaded dataset into the datasets directory
mv /path/to/annotated_dataset_skillgen.hdf5 datasets/annotated_dataset_skillgen.hdf5
Tip
A major advantage of SkillGen is that the same annotated dataset can be reused across multiple related tasks (e.g., basic stacking and adaptive bin stacking). This avoids collecting and annotating new data per variant.
{Optional for the tasks in this tutorial} Collect a fresh dataset (source + annotated)
If you want to collect a fresh source dataset and then create an annotated dataset for SkillGen, follow these commands. The user is expected to have knowledge of the Isaac Lab Mimic workflow.
Important pointers before you begin
Using the provided annotated dataset is the fastest path to get started with SkillGen tasks in this tutorial.
If you create your own dataset, SkillGen requires manual annotation of both subtask start and termination boundaries (no auto-annotation).
Start boundary signals are mandatory for SkillGen; use
--annotate_subtask_start_signalsduring annotation or data generation will fail.Keep your subtask definitions (
object_ref,subtask_term_signal) consistent with the SkillGen environment config.
Record demonstrations (any teleop device is supported; replace spacemouse if needed):
./isaaclab.sh -p scripts/tools/record_demos.py \
--task Isaac-Stack-Cube-Franka-IK-Rel-Skillgen-v0 \
--teleop_device spacemouse \
--dataset_file ./datasets/dataset_skillgen.hdf5 \
--num_demos 10
Annotate demonstrations for SkillGen (writes both term and start boundaries):
./isaaclab.sh -p scripts/imitation_learning/isaaclab_mimic/annotate_demos.py \
--device cpu \
--task Isaac-Stack-Cube-Franka-IK-Rel-Skillgen-v0 \
--input_file ./datasets/dataset_skillgen.hdf5 \
--output_file ./datasets/annotated_dataset_skillgen.hdf5 \
--annotate_subtask_start_signals
Understanding Dataset Annotation#
SkillGen requires datasets with annotated subtask start and termination boundaries. Auto-annotation is not supported.
Subtasks in SkillGen#
Technical definition: A subtask is a contiguous demo segment that achieves a manipulation objective, defined via SubTaskConfig:
object_ref: the object (orNone) used as the spatial reference for this subtasksubtask_term_signal: the binary termination signal name (transitions 0 to 1 when the subtask completes)subtask_start_signal: the binary start signal name (transitions 0 to 1 when the subtask begins; required for SkillGen)
The subtask localization process performs:
detection of signal transition points (0 to 1) to identify subtask boundaries
[t_start, t_end];extraction of the subtask segment between boundaries;
computation of end-effector trajectories and key poses in an object- or task-relative frame (using
object_refif provided);
This converts absolute, scene-specific motions into object-relative skill segments that can be adapted to new object placements and scene configurations during data generation.
Manual Annotation Workflow#
Contrary to the Isaac Lab Mimic workflow, SkillGen requires manual annotation of subtask start and termination boundaries. For example, for grasping a cube, the start signal is right before the gripper closes and the termination signal is right after the object is grasped. You can adjust the start and termination signals to fit your subtask definition.
Tip
Manual Annotation Controls:
Press
Nto start/continue playbackPress
Bto pausePress
Sto mark subtask boundaryPress
Qto skip current demonstration
When annotating the start and end signals for a skill segment (e.g., grasp, stack, etc.), pause the playback using B a few steps before the skill, annotate the start signal using S, and then resume playback using N. After the skill is completed, pause again a few steps later to annotate the end signal using S.
Data Generation with SkillGen#
SkillGen transforms annotated demonstrations into diverse, high-quality datasets using motion planning.
How SkillGen Works#
The SkillGen pipeline uses your annotated dataset and the environment’s Mimic API to synthesize new demonstrations:
Subtask boundary use: Reads per-subtask start and termination indices from the annotated dataset
Goal sampling: Samples target poses per subtask according to task constraints and datagen config
Trajectory planning: Plans collision-free motions between subtask segments using cuRobo (when
--use_skillgen)Trajectory stitching: Stitches skill segments and planned trajectories into complete demonstrations.
Success evaluation: Validates task success terms; only successful trials are written to the output dataset
Usage Parameters#
Key parameters for SkillGen data generation:
--use_skillgen: Enables SkillGen planner (required)--generation_num_trials: Number of demonstrations to generate--num_envs: Parallel environments (tune based on GPU memory)--device: Computation device (cpu/cuda). Use cpu for stable physics--headless: Disable visualization for faster generation
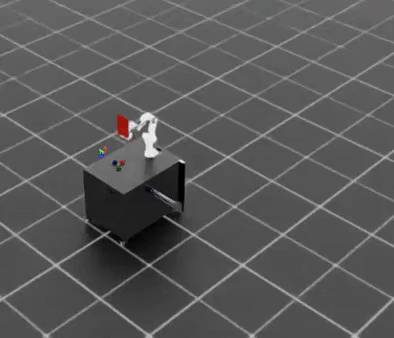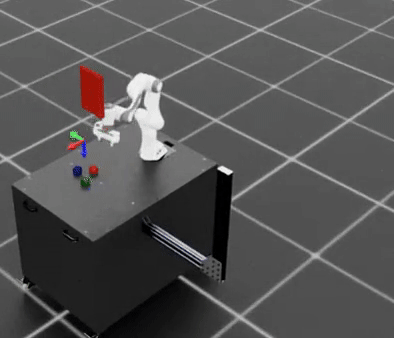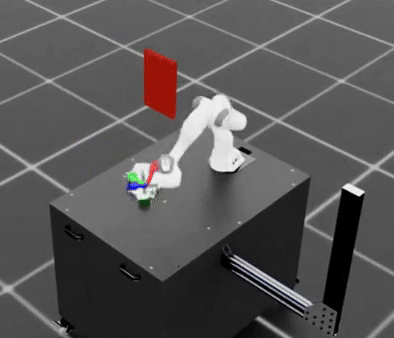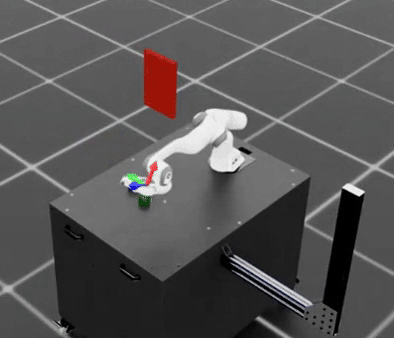
Task 1: Basic Cube Stacking#
Generate demonstrations for the standard Isaac Lab Mimic cube stacking task. In this task, the Franka robot must:
Pick up the red cube and place it on the blue cube
Pick up the green cube and place it on the red cube
Final stack order: blue (bottom), red (middle), green (top).
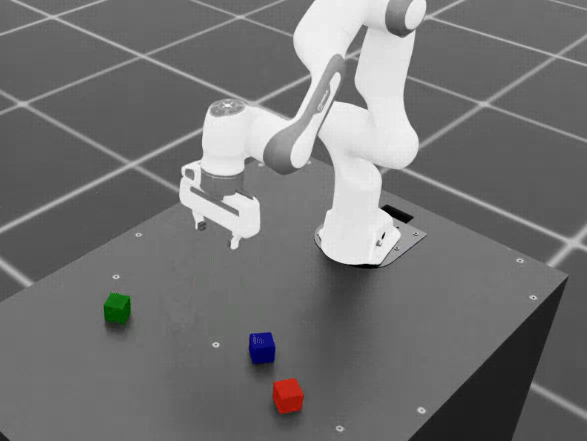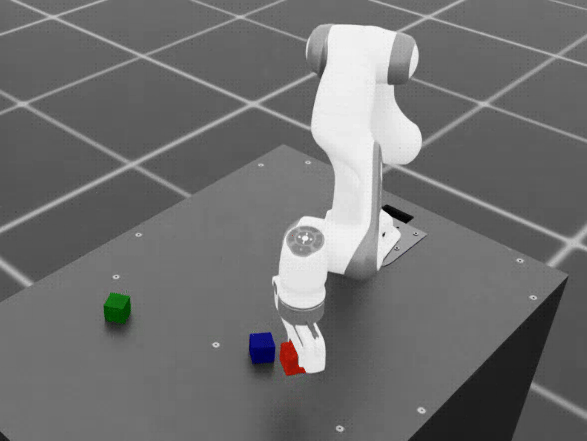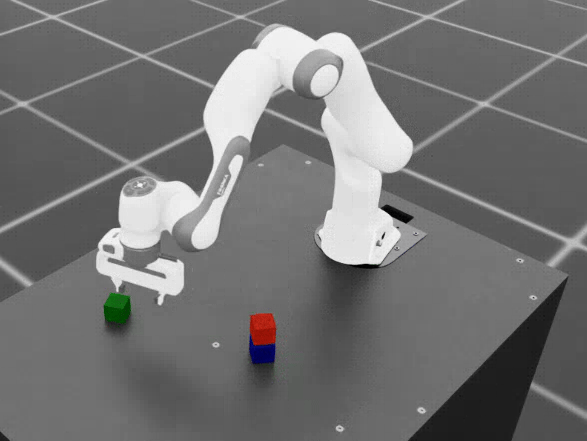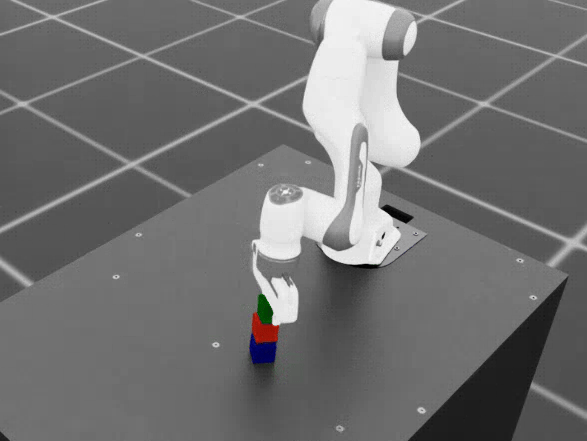
Cube stacking dataset example.#
Small-Scale Generation#
Start with a small dataset to verify everything works:
./isaaclab.sh -p scripts/imitation_learning/isaaclab_mimic/generate_dataset.py \
--device cpu \
--num_envs 1 \
--generation_num_trials 10 \
--input_file ./datasets/annotated_dataset_skillgen.hdf5 \
--output_file ./datasets/generated_dataset_small_skillgen_cube_stack.hdf5 \
--task Isaac-Stack-Cube-Franka-IK-Rel-Skillgen-v0 \
--use_skillgen
Full-Scale Generation#
Once satisfied with small-scale results, generate a full training dataset:
./isaaclab.sh -p scripts/imitation_learning/isaaclab_mimic/generate_dataset.py \
--device cpu \
--headless \
--num_envs 1 \
--generation_num_trials 1000 \
--input_file ./datasets/annotated_dataset_skillgen.hdf5 \
--output_file ./datasets/generated_dataset_skillgen_cube_stack.hdf5 \
--task Isaac-Stack-Cube-Franka-IK-Rel-Skillgen-v0 \
--use_skillgen
Note
Use
--headlessto disable visualization for faster generation. Rerun visualization can be enabled by settingvisualize_plan = Truein the cuRobo planner configuration with--headlessenabled as well for debugging.Adjust
--num_envsbased on your GPU memory (start with 1, increase gradually). The performance gain is not very significant when num_envs is greater than 1. A value of 5 seems to be a sweet spot for most GPUs to balance performance and memory usage between cuRobo instances and simulation environments.Generation time: ~90 to 120 minutes for one environment with
--headlessenabled for 1000 demonstrations on a RTX 6000 Ada GPU. Time depends on the GPU, the number of environments, and the success rate of the demonstrations (which depends on quality of the annotated dataset).cuRobo planner interface and configurations are described in cuRobo Interface Features.
Task 2: Adaptive Cube Stacking in a Bin#
SkillGen can also be used to generate datasets for adaptive tasks. In this example, we generate a dataset for adaptive cube stacking in a narrow bin. The bin is placed at a fixed position and orientation in the workspace and a blue cube is placed at the center of the bin. The robot must generate successful demonstrations for stacking the red and green cubes on the blue cube without colliding with the bin.
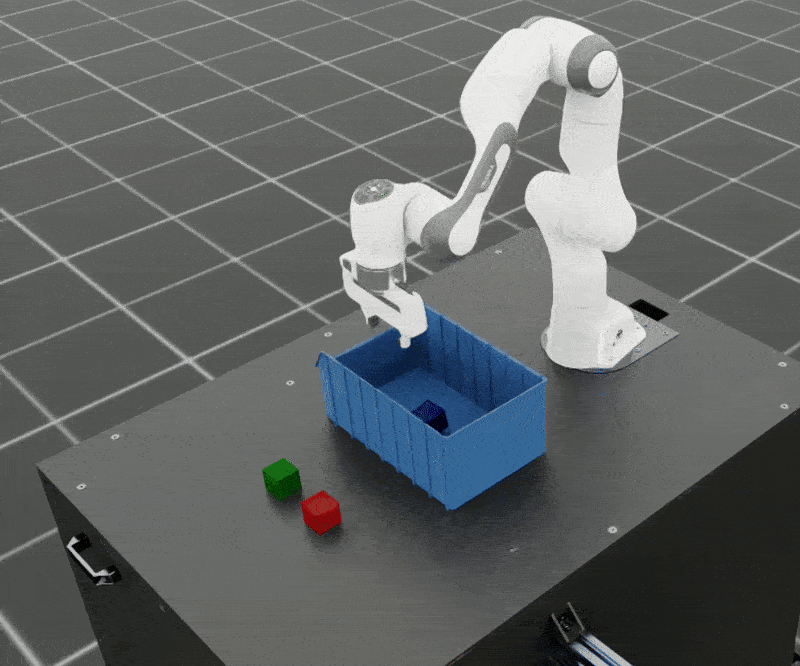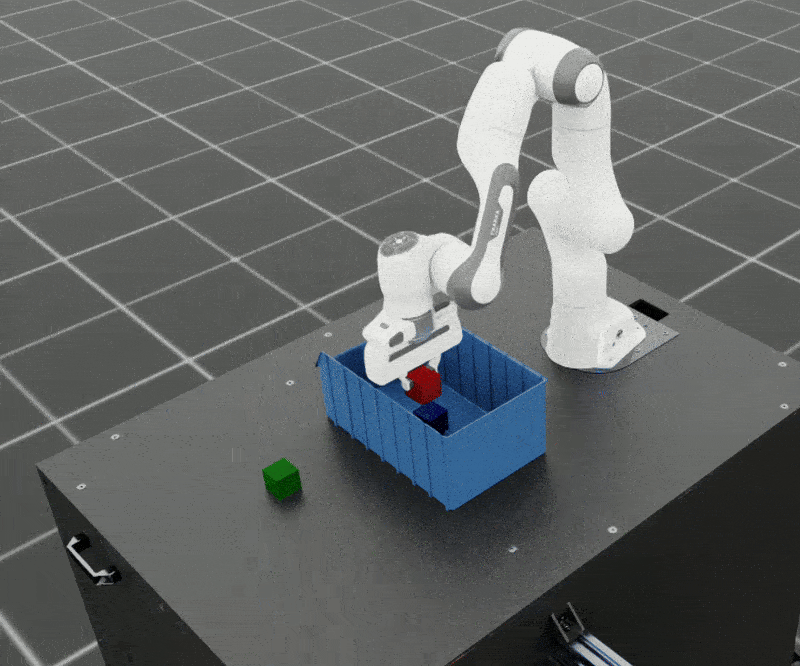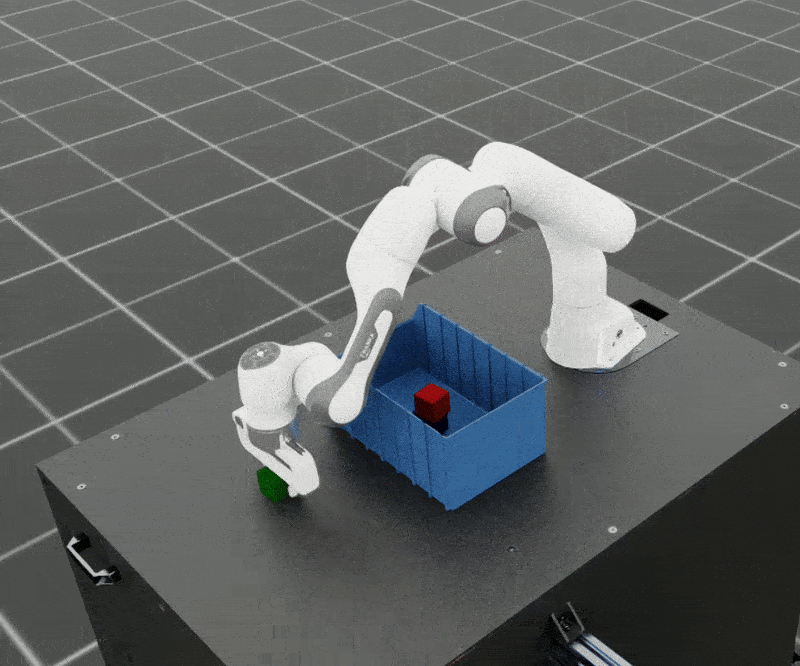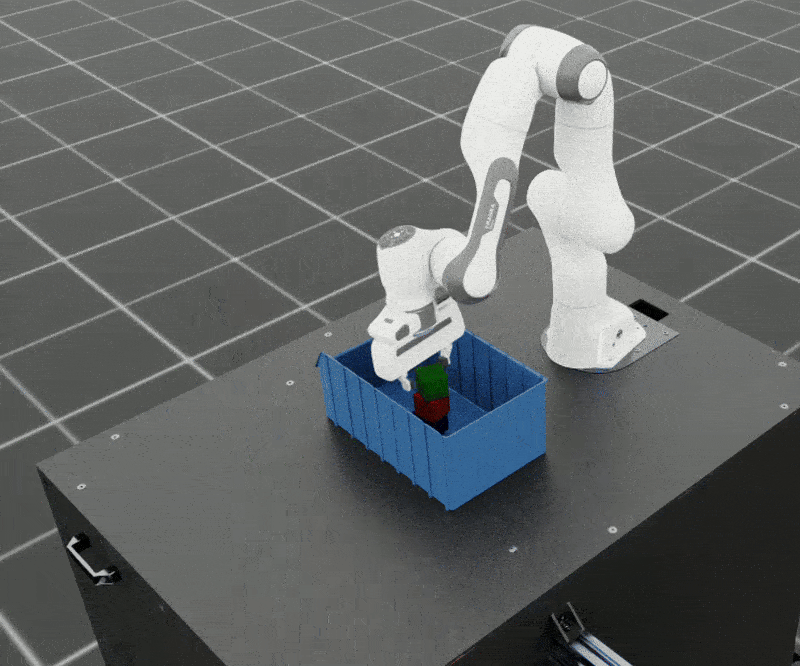
Adaptive bin stacking data generation example.#
Small-Scale Generation#
Test the adaptive stacking setup:
./isaaclab.sh -p scripts/imitation_learning/isaaclab_mimic/generate_dataset.py \
--device cpu \
--num_envs 1 \
--generation_num_trials 10 \
--input_file ./datasets/annotated_dataset_skillgen.hdf5 \
--output_file ./datasets/generated_dataset_small_skillgen_bin_cube_stack.hdf5 \
--task Isaac-Stack-Cube-Bin-Franka-IK-Rel-Mimic-v0 \
--use_skillgen
Full-Scale Generation#
Generate the complete adaptive stacking dataset:
./isaaclab.sh -p scripts/imitation_learning/isaaclab_mimic/generate_dataset.py \
--device cpu \
--headless \
--num_envs 1 \
--generation_num_trials 1000 \
--input_file ./datasets/annotated_dataset_skillgen.hdf5 \
--output_file ./datasets/generated_dataset_skillgen_bin_cube_stack.hdf5 \
--task Isaac-Stack-Cube-Bin-Franka-IK-Rel-Mimic-v0 \
--use_skillgen
Warning
Adaptive tasks typically have lower success rates and higher data generation time due to increased complexity. The time taken to generate the dataset is also longer due to lower success rates than vanilla cube stacking and difficult planning problems.
Note
If the pre-annotated dataset is used and the data generation command is run with --headless enabled, the generation time is typically around ~220 minutes for 1000 demonstrations for a single environment on a RTX 6000 Ada GPU.
Note
VRAM usage and GPU recommendations
- Figures measured over 10 generated demonstrations on an RTX 6000 Ada.
Vanilla Cube Stacking: 1 env ~9.3–9.6 GB steady; 5 envs ~21.8–22.2 GB steady (briefly higher during initialization).
Adaptive Bin Cube Stacking: 1 env ~9.3–9.6 GB steady; 5 envs ~22.0–22.3 GB steady (briefly higher during initialization).
Minimum recommended GPU: ≥24 GB VRAM for
--num_envs1–2; ≥48 GB VRAM for--num_envsup to ~5.To reduce VRAM: prefer
--headlessand keep--num_envsmodest. Numbers can vary with scene assets and number of demonstrations.
Learning Policies from SkillGen Data#
Similar to the Isaac Lab Mimic workflow, you can train imitation learning policies using the generated SkillGen datasets with Robomimic.
Basic Cube Stacking Policy#
Train a state-based policy for the basic cube stacking task:
./isaaclab.sh -p scripts/imitation_learning/robomimic/train.py \
--task Isaac-Stack-Cube-Franka-IK-Rel-Skillgen-v0 \
--algo bc \
--dataset ./datasets/generated_dataset_skillgen_cube_stack.hdf5
Adaptive Bin Cube Stacking Policy#
Train a policy for the more complex adaptive bin stacking:
./isaaclab.sh -p scripts/imitation_learning/robomimic/train.py \
--task Isaac-Stack-Cube-Bin-Franka-IK-Rel-Mimic-v0 \
--algo bc \
--dataset ./datasets/generated_dataset_skillgen_bin_cube_stack.hdf5
Note
The training script will save the model checkpoints in the model directory under IssacLab/logs/robomimic.
Evaluating Trained Policies#
Test your trained policies:
# Basic cube stacking evaluation
./isaaclab.sh -p scripts/imitation_learning/robomimic/play.py \
--device cpu \
--task Isaac-Stack-Cube-Franka-IK-Rel-Skillgen-v0 \
--num_rollouts 50 \
--checkpoint /path/to/model_checkpoint.pth
# Adaptive bin cube stacking evaluation
./isaaclab.sh -p scripts/imitation_learning/robomimic/play.py \
--device cpu \
--task Isaac-Stack-Cube-Bin-Franka-IK-Rel-Mimic-v0 \
--num_rollouts 50 \
--checkpoint /path/to/model_checkpoint.pth
Note
Expected Success Rates and Recommendations for Cube Stacking and Bin Cube Stacking Tasks
SkillGen data generation and downstream policy success are sensitive to the task and the quality of dataset annotation, and can show high variance.
For cube stacking and bin cube stacking, data generation success is typically 40% to 70% when the dataset is properly annotated per the instructions.
Behavior Cloning (BC) policy success from 1000 generated demonstrations trained for 2000 epochs (default) is typically 40% to 85% for these tasks, depending on data quality.
Training the policy with 1000 demonstrations and for 2000 epochs takes about 30 to 35 minutes on a RTX 6000 Ada GPU. Training time increases with the number of demonstrations and epochs.
For dataset generation time, see Task 1: Basic Cube Stacking and Task 2: Adaptive Cube Stacking in a Bin.
Recommendation: Train for the default 2000 epochs with about 1000 generated demonstrations, and evaluate multiple checkpoints saved after the 1000th epoch to select the best-performing policy.
cuRobo Interface Features#
This section summarizes the cuRobo planner interface and features. The SkillGen pipeline uses the cuRobo planner to generate collision-free motions between subtask segments. However, the user can use cuRobo as a standalone motion planner for your own tasks. The user can also implement their own motion planner by subclassing the base motion planner and implementing the same API.
Base Motion Planner (Extensible)#
Location:
isaaclab_mimic/motion_planners/base_motion_planner.pyPurpose: Uniform interface for all motion planners used by SkillGen
Extensibility: New planners can be added by subclassing and implementing the same API; SkillGen consumes the API without code changes
cuRobo Planner (GPU, collision-aware)#
Location:
isaaclab_mimic/motion_planners/curoboMulti-phase planning:
Retreat → Contact → Approach phases per subtask
Configurable collision filtering in contact phases
For SkillGen, retreat and approach phases are collision-free. The transit phase is collision-checked.
World synchronization:
Updates robot state, attached objects, and collision spheres from the Isaac Lab scene each trial
Dynamic attach/detach of objects during grasp/place
Collision representation:
Contact-aware sphere sets with per-phase enables/filters
Outputs:
Time-parameterized, collision-checked trajectories for stitching
Tests:
source/isaaclab_mimic/test/test_curobo_planner_cube_stack.pysource/isaaclab_mimic/test/test_curobo_planner_franka.pysource/isaaclab_mimic/test/test_generate_dataset_skillgen.py
These tests can also serve as a reference for how to use cuRobo as a standalone motion planner.
Note
For detailed cuRobo config creation and parameters, please see the file isaaclab_mimic/motion_planners/curobo/curobo_planner_config.py.
Generation Pipeline Integration#
When --use_skillgen is enabled in generate_dataset.py, the following pipeline is executed:
Randomize subtask boundaries: Randomize per-demo start and termination indices for each subtask using task-configured offset ranges.
Build per-subtask trajectories: For each end-effector and subtask:
Select a source demonstration segment (strategy-driven; respects coordination/sequential constraints)
Transform the segment to the current scene (object-relative or coordination delta; optional first-pose interpolation)
Wrap the transformed segment into a waypoint trajectory
Transition between subtasks: - Plan a collision-aware transition with cuRobo to the subtask’s first waypoint (world sync, optional attach/detach), execute the planned waypoints, then resume the subtask trajectory
Execute with constraints: - Execute waypoints step-by-step across end-effectors while enforcing subtask constraints (sequential, coordination with synchronous steps); optionally update planner visualization if enabled
Record and export: - Accumulate states/observations/actions, set the episode success flag, and export the episode (the outer pipeline filters/consumes successes)
Visualization and Debugging#
Users can visualize the planned trajectories and debug for collisions using Rerun-based plan visualizer. This can be enabled by setting visualize_plan = True in the cuRobo planner configuration. Note that rerun needs to be installed to visualize the planned trajectories. Refer to Step 3 in Installation for installation instructions.
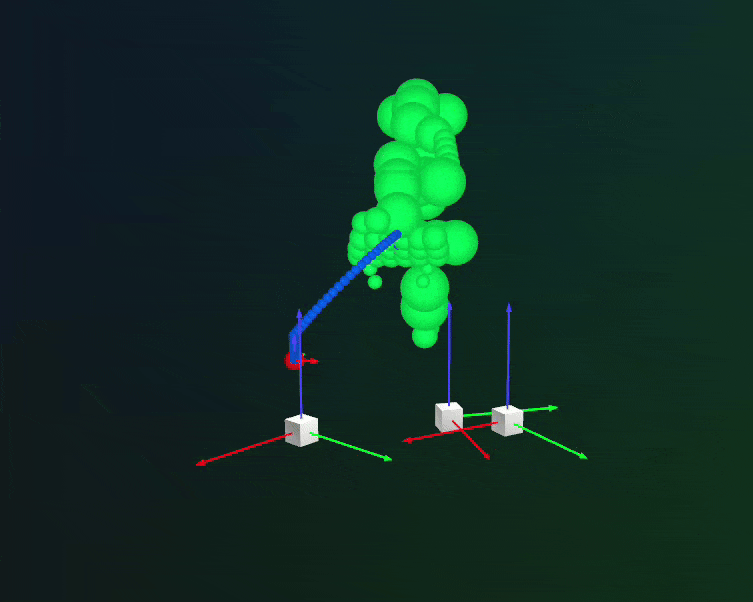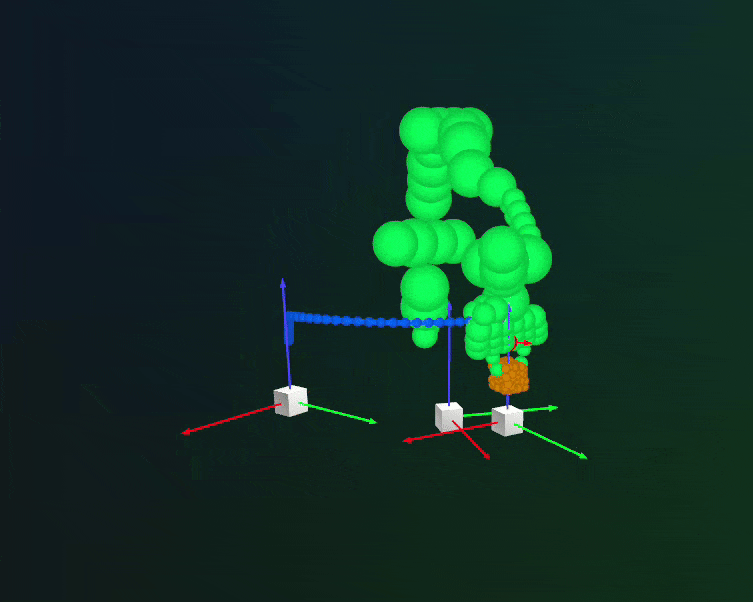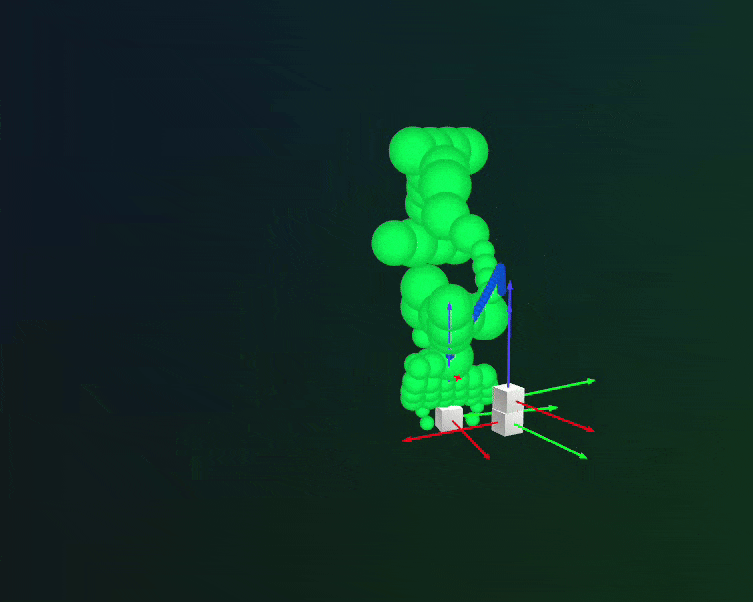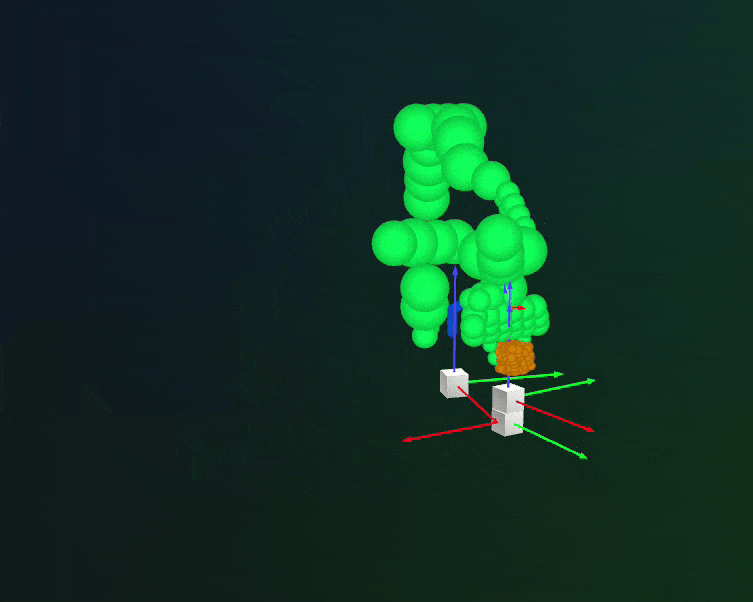
Rerun integration: planned trajectories with collision spheres.#
Note
Check cuRobo usage license in docs/licenses/dependencies/cuRobo-license.txt