Frame Transformer#
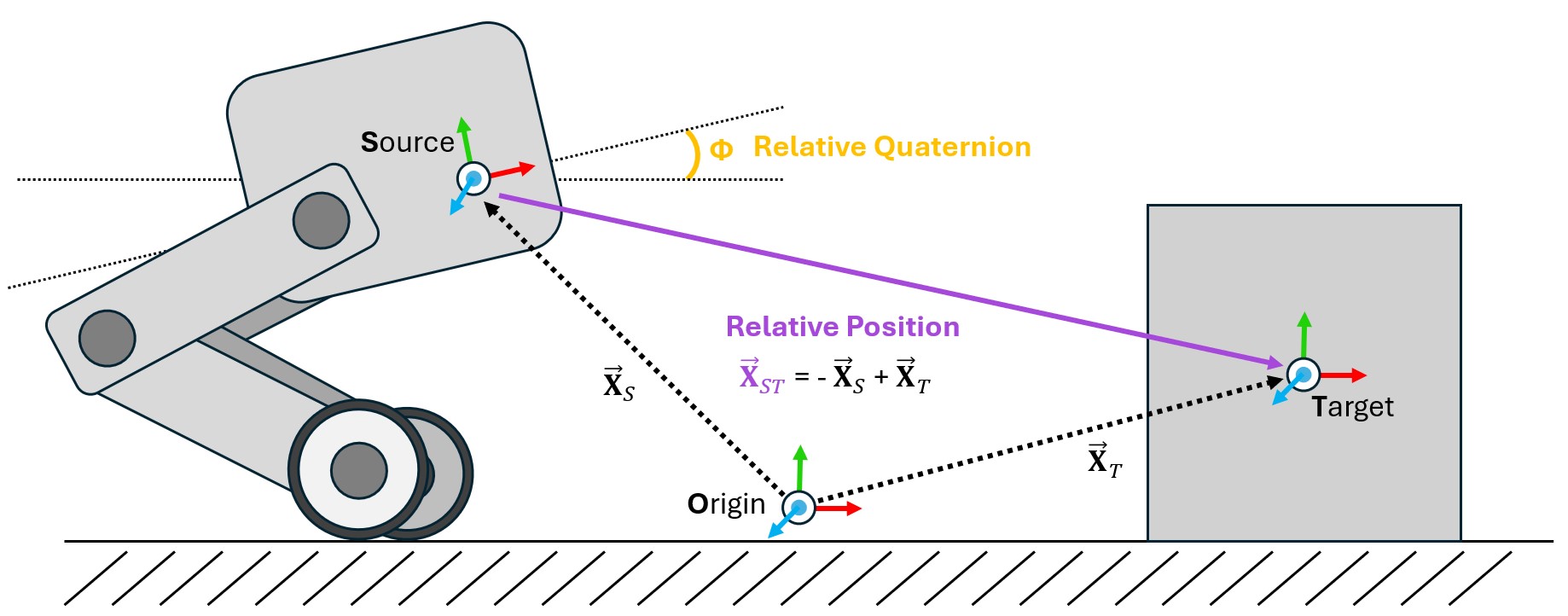
One of the most common operations that needs to be performed within a physics simulation is the frame transformation: rewriting a vector or quaternion in the basis of an arbitrary euclidean coordinate system. There are many ways to accomplish this within Isaac and USD, but these methods can be cumbersome to implement within Isaac Lab’s GPU based simulation and cloned environments. To mitigate this problem, we have designed the Frame Transformer Sensor, that tracks and calculate the relative frame transformations for rigid bodies of interest to the scene.
The sensory is minimally defined by a source frame and a list of target frames. These definitions take the form of a prim path (for the source) and list of regex capable prim paths the rigid bodies to be tracked (for the targets).
@configclass
class FrameTransformerSensorSceneCfg(InteractiveSceneCfg):
"""Design the scene with sensors on the robot."""
# ground plane
ground = AssetBaseCfg(prim_path="/World/defaultGroundPlane", spawn=sim_utils.GroundPlaneCfg())
# lights
dome_light = AssetBaseCfg(
prim_path="/World/Light", spawn=sim_utils.DomeLightCfg(intensity=3000.0, color=(0.75, 0.75, 0.75))
)
# robot
robot = ANYMAL_C_CFG.replace(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot")
# Rigid Object
cube = RigidObjectCfg(
prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Cube",
spawn=sim_utils.CuboidCfg(
size=(1, 1, 1),
rigid_props=sim_utils.RigidBodyPropertiesCfg(),
mass_props=sim_utils.MassPropertiesCfg(mass=100.0),
collision_props=sim_utils.CollisionPropertiesCfg(),
physics_material=sim_utils.RigidBodyMaterialCfg(static_friction=1.0),
visual_material=sim_utils.PreviewSurfaceCfg(diffuse_color=(0.0, 1.0, 0.0), metallic=0.2),
),
init_state=RigidObjectCfg.InitialStateCfg(pos=(5, 0, 0.5)),
)
specific_transforms = FrameTransformerCfg(
prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/base",
target_frames=[
FrameTransformerCfg.FrameCfg(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/LF_FOOT"),
FrameTransformerCfg.FrameCfg(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/RF_FOOT"),
],
debug_vis=True,
)
cube_transform = FrameTransformerCfg(
prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/base",
target_frames=[FrameTransformerCfg.FrameCfg(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Cube")],
debug_vis=False,
)
robot_transforms = FrameTransformerCfg(
prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/base",
target_frames=[FrameTransformerCfg.FrameCfg(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/.*")],
debug_vis=False,
)
We can now run the scene and query the sensor for data
def run_simulator(sim: sim_utils.SimulationContext, scene: InteractiveScene):
.
.
.
# Simulate physics
while simulation_app.is_running():
.
.
.
# print information from the sensors
print("-------------------------------")
print(scene["specific_transforms"])
print("relative transforms:", scene["specific_transforms"].data.target_pos_source)
print("relative orientations:", scene["specific_transforms"].data.target_quat_source)
print("-------------------------------")
print(scene["cube_transform"])
print("relative transform:", scene["cube_transform"].data.target_pos_source)
print("-------------------------------")
print(scene["robot_transforms"])
print("relative transforms:", scene["robot_transforms"].data.target_pos_source)
Let’s take a look at the result for tracking specific objects. First, we can take a look at the data coming from the sensors on the feet
-------------------------------
FrameTransformer @ '/World/envs/env_.*/Robot/base':
tracked body frames: ['base', 'LF_FOOT', 'RF_FOOT']
number of envs: 1
source body frame: base
target frames (count: ['LF_FOOT', 'RF_FOOT']): 2
relative transforms: tensor([[[ 0.4658, 0.3085, -0.4840],
[ 0.4487, -0.2959, -0.4828]]], device='cuda:0')
relative orientations: tensor([[[ 0.9623, 0.0072, -0.2717, -0.0020],
[ 0.9639, 0.0052, -0.2663, -0.0014]]], device='cuda:0')
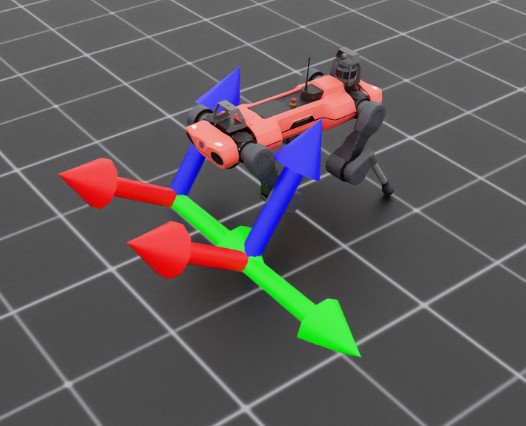
By activating the visualizer, we can see that the frames of the feet are rotated “upward” slightly. We can also see the explicit relative positions and rotations by querying the sensor for data, which returns these values as a list with the same order as the tracked frames. This becomes even more apparent if we examine the transforms specified by regex.
-------------------------------
FrameTransformer @ '/World/envs/env_.*/Robot/base':
tracked body frames: ['base', 'LF_FOOT', 'LF_HIP', 'LF_SHANK', 'LF_THIGH', 'LH_FOOT', 'LH_HIP', 'LH_SHANK', 'LH_THIGH', 'RF_FOOT', 'RF_HIP', 'RF_SHANK', 'RF_THIGH', 'RH_FOOT', 'RH_HIP', 'RH_SHANK', 'RH_THIGH', 'base']
number of envs: 1
source body frame: base
target frames (count: ['LF_FOOT', 'LF_HIP', 'LF_SHANK', 'LF_THIGH', 'LH_FOOT', 'LH_HIP', 'LH_SHANK', 'LH_THIGH', 'RF_FOOT', 'RF_HIP', 'RF_SHANK', 'RF_THIGH', 'RH_FOOT', 'RH_HIP', 'RH_SHANK', 'RH_THIGH', 'base']): 17
relative transforms: tensor([[[ 4.6581e-01, 3.0846e-01, -4.8398e-01],
[ 2.9990e-01, 1.0400e-01, -1.7062e-09],
[ 2.1409e-01, 2.9177e-01, -2.4214e-01],
[ 3.5980e-01, 1.8780e-01, 1.2608e-03],
[-4.8813e-01, 3.0973e-01, -4.5927e-01],
[-2.9990e-01, 1.0400e-01, 2.7044e-09],
[-2.1495e-01, 2.9264e-01, -2.4198e-01],
[-3.5980e-01, 1.8780e-01, 1.5582e-03],
[ 4.4871e-01, -2.9593e-01, -4.8277e-01],
[ 2.9990e-01, -1.0400e-01, -2.7057e-09],
[ 1.9971e-01, -2.8554e-01, -2.3778e-01],
[ 3.5980e-01, -1.8781e-01, -9.1049e-04],
[-5.0090e-01, -2.9095e-01, -4.5746e-01],
[-2.9990e-01, -1.0400e-01, 6.3592e-09],
[-2.1860e-01, -2.8251e-01, -2.5163e-01],
[-3.5980e-01, -1.8779e-01, -1.8792e-03],
[ 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00]]], device='cuda:0')
Here, the sensor is tracking all rigid body children of Robot/base, but this expression is inclusive, meaning that the source body itself is also a target. This can be seen both by examining the source and target list, where base appears twice, and also in the returned data, where the sensor returns the relative transform to itself, (0, 0, 0).
Code for frame_transformer_sensor.py
1# Copyright (c) 2022-2026, The Isaac Lab Project Developers (https://github.com/isaac-sim/IsaacLab/blob/main/CONTRIBUTORS.md).
2# All rights reserved.
3#
4# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
5
6import argparse
7
8from isaaclab.app import AppLauncher
9
10# add argparse arguments
11parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Example on using the frame transformer sensor.")
12parser.add_argument("--num_envs", type=int, default=1, help="Number of environments to spawn.")
13# append AppLauncher cli args
14AppLauncher.add_app_launcher_args(parser)
15# parse the arguments
16args_cli = parser.parse_args()
17
18# launch omniverse app
19app_launcher = AppLauncher(args_cli)
20simulation_app = app_launcher.app
21
22"""Rest everything follows."""
23
24import torch
25
26import isaaclab.sim as sim_utils
27from isaaclab.assets import AssetBaseCfg, RigidObjectCfg
28from isaaclab.scene import InteractiveScene, InteractiveSceneCfg
29from isaaclab.sensors import FrameTransformerCfg
30from isaaclab.utils import configclass
31
32##
33# Pre-defined configs
34##
35from isaaclab_assets.robots.anymal import ANYMAL_C_CFG # isort: skip
36
37
38@configclass
39class FrameTransformerSensorSceneCfg(InteractiveSceneCfg):
40 """Design the scene with sensors on the robot."""
41
42 # ground plane
43 ground = AssetBaseCfg(prim_path="/World/defaultGroundPlane", spawn=sim_utils.GroundPlaneCfg())
44
45 # lights
46 dome_light = AssetBaseCfg(
47 prim_path="/World/Light", spawn=sim_utils.DomeLightCfg(intensity=3000.0, color=(0.75, 0.75, 0.75))
48 )
49
50 # robot
51 robot = ANYMAL_C_CFG.replace(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot")
52
53 # Rigid Object
54 cube = RigidObjectCfg(
55 prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Cube",
56 spawn=sim_utils.CuboidCfg(
57 size=(1, 1, 1),
58 rigid_props=sim_utils.RigidBodyPropertiesCfg(),
59 mass_props=sim_utils.MassPropertiesCfg(mass=100.0),
60 collision_props=sim_utils.CollisionPropertiesCfg(),
61 physics_material=sim_utils.RigidBodyMaterialCfg(static_friction=1.0),
62 visual_material=sim_utils.PreviewSurfaceCfg(diffuse_color=(0.0, 1.0, 0.0), metallic=0.2),
63 ),
64 init_state=RigidObjectCfg.InitialStateCfg(pos=(5, 0, 0.5)),
65 )
66
67 specific_transforms = FrameTransformerCfg(
68 prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/base",
69 target_frames=[
70 FrameTransformerCfg.FrameCfg(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/LF_FOOT"),
71 FrameTransformerCfg.FrameCfg(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/RF_FOOT"),
72 ],
73 debug_vis=True,
74 )
75
76 cube_transform = FrameTransformerCfg(
77 prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/base",
78 target_frames=[FrameTransformerCfg.FrameCfg(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Cube")],
79 debug_vis=False,
80 )
81
82 robot_transforms = FrameTransformerCfg(
83 prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/base",
84 target_frames=[FrameTransformerCfg.FrameCfg(prim_path="{ENV_REGEX_NS}/Robot/.*")],
85 debug_vis=False,
86 )
87
88
89def run_simulator(sim: sim_utils.SimulationContext, scene: InteractiveScene):
90 """Run the simulator."""
91 # Define simulation stepping
92 sim_dt = sim.get_physics_dt()
93 sim_time = 0.0
94 count = 0
95
96 # Simulate physics
97 while simulation_app.is_running():
98 if count % 500 == 0:
99 # reset counter
100 count = 0
101 # reset the scene entities
102 # root state
103 # we offset the root state by the origin since the states are written in simulation world frame
104 # if this is not done, then the robots will be spawned at the (0, 0, 0) of the simulation world
105 root_state = scene["robot"].data.default_root_state.clone()
106 root_state[:, :3] += scene.env_origins
107 scene["robot"].write_root_pose_to_sim(root_state[:, :7])
108 scene["robot"].write_root_velocity_to_sim(root_state[:, 7:])
109 # set joint positions with some noise
110 joint_pos, joint_vel = (
111 scene["robot"].data.default_joint_pos.clone(),
112 scene["robot"].data.default_joint_vel.clone(),
113 )
114 joint_pos += torch.rand_like(joint_pos) * 0.1
115 scene["robot"].write_joint_state_to_sim(joint_pos, joint_vel)
116 # clear internal buffers
117 scene.reset()
118 print("[INFO]: Resetting robot state...")
119 # Apply default actions to the robot
120 # -- generate actions/commands
121 targets = scene["robot"].data.default_joint_pos
122 # -- apply action to the robot
123 scene["robot"].set_joint_position_target(targets)
124 # -- write data to sim
125 scene.write_data_to_sim()
126 # perform step
127 sim.step()
128 # update sim-time
129 sim_time += sim_dt
130 count += 1
131 # update buffers
132 scene.update(sim_dt)
133
134 # print information from the sensors
135 print("-------------------------------")
136 print(scene["specific_transforms"])
137 print("relative transforms:", scene["specific_transforms"].data.target_pos_source)
138 print("relative orientations:", scene["specific_transforms"].data.target_quat_source)
139 print("-------------------------------")
140 print(scene["cube_transform"])
141 print("relative transform:", scene["cube_transform"].data.target_pos_source)
142 print("-------------------------------")
143 print(scene["robot_transforms"])
144 print("relative transforms:", scene["robot_transforms"].data.target_pos_source)
145
146
147def main():
148 """Main function."""
149
150 # Initialize the simulation context
151 sim_cfg = sim_utils.SimulationCfg(dt=0.005, device=args_cli.device)
152 sim = sim_utils.SimulationContext(sim_cfg)
153 # Set main camera
154 sim.set_camera_view(eye=[3.5, 3.5, 3.5], target=[0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
155 # design scene
156 scene_cfg = FrameTransformerSensorSceneCfg(num_envs=args_cli.num_envs, env_spacing=2.0)
157 scene = InteractiveScene(scene_cfg)
158 # Play the simulator
159 sim.reset()
160 # Now we are ready!
161 print("[INFO]: Setup complete...")
162 # Run the simulator
163 run_simulator(sim, scene)
164
165
166if __name__ == "__main__":
167 # run the main function
168 main()
169 # close sim app
170 simulation_app.close()

